Multiple host proteins that function in phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate metabolism are recruited to the chlamydial inclusion
- PMID: 20231409
- PMCID: PMC2863499
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01340-09
Multiple host proteins that function in phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate metabolism are recruited to the chlamydial inclusion
Abstract
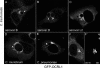
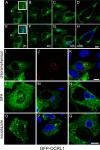
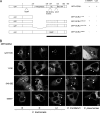
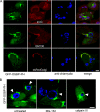
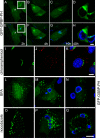
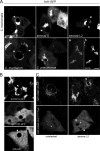
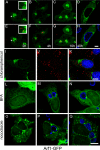
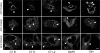
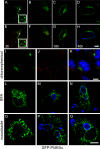
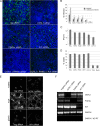
Chlamydiae replicate within a nonacidified vacuole, termed an inclusion. As obligate intracellular bacteria, chlamydiae actively modify their vacuole to exploit host signaling and trafficking pathways. Recently, we demonstrated that several Rab GTPases are actively targeted to the inclusion. To define the biological roles of inclusion localized Rab GTPases, we have begun to identify inclusion-localized Rab effectors. Here we demonstrate that oculocerebrorenal syndrome of Lowe protein 1 (OCRL1), a Golgi complex-localized phosphatidylinositol (PI)-5-phosphatase that binds to multiple Rab GTPases, localizes to chlamydial inclusions. By examining the intracellular localization of green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion proteins that bind to unique phosphoinositide species, we also demonstrate that phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P), the product of OCRL1, is present at the inclusion membrane. Furthermore, two additional host proteins, Arf1, which together with PI4P mediates the recruitment of PI4P-binding proteins to the Golgi complex, and PI4KII alpha, a major producer of Golgi complex-localized PI4P, also localize to chlamydial inclusions. Depletion of OCRL1, Arf1, or PI4KII alpha by small interfering RNA (siRNA) decreases inclusion formation and the production of infectious progeny. Infectivity is further decreased in cells simultaneously depleted for all three host proteins, suggesting partially overlapping functions in infected cells. Collectively, these data demonstrate that Chlamydia species create a unique replication-competent vacuolar environment by modulating both the Rab GTPase and the PI composition of the chlamydial inclusion.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rab GTPases are recruited to chlamydial inclusions in both a species-dependent and species-independent manner.Infect Immun. 2003 Oct;71(10):5855-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.5855-5870.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 14500507 Free PMC article.
-
The Rab6 effector Bicaudal D1 associates with Chlamydia trachomatis inclusions in a biovar-specific manner.Infect Immun. 2007 Feb;75(2):781-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01447-06. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17101644 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae inclusion membrane protein Cpn0585 interacts with multiple Rab GTPases.Infect Immun. 2007 Dec;75(12):5586-96. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01020-07. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17908815 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the Rab binding domain of OCRL1 in complex with Rab8 and functional implications of the OCRL1/Rab8 module for Lowe syndrome.Small GTPases. 2012 Apr-Jun;3(2):107-10. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.19380. Small GTPases. 2012. PMID: 22790198 Review.
-
The chlamydial inclusion: escape from the endocytic pathway.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002;18:221-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.18.012502.105845. Epub 2002 Apr 2. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12142274 Review.
Cited by
-
Chlamydia cell biology and pathogenesis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Jun;14(6):385-400. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.30. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27108705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishing the intracellular niche of obligate intracellular vacuolar pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 14;13:1206037. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1206037. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37645379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host HDL biogenesis machinery is recruited to the inclusion of Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells and regulates chlamydial growth.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Oct;14(10):1497-512. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01823.x. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22672264 Free PMC article.
-
NK Cell-Mediated Processing Of Chlamydia psittaci Drives Potent Anti-Bacterial Th1 Immunity.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 18;9(1):4799. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41264-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30886314 Free PMC article.
-
Idiosyncratic Biogenesis of Intracellular Pathogens-Containing Vacuoles.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 11;11:722433. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.722433. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34858868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Attree, O., I. M. Olivos, I. Okabe, L. C. Bailey, D. L. Nelson, R. A. Lewis, R. R. McInnes, and R. L. Nussbaum. 1992. The Lowe's oculocerebrorenal syndrome gene encodes a protein highly homologous to inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase. Nature 358:239-242. - PubMed
-
- Balana, M. E., F. Niedergand, A. Subtil, A. Alcover, P. Chavrier, and A. Dautry-Varsat. 2005. Arf6 GTPase controls bacterial invasion by actin remodeling. J. Cell Sci. 118:2201-2210. - PubMed
-
- Balla, A., and T. Balla. 2006. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases: old enzymes with emerging functions. Trends Cell Biol. 16:351-361. - PubMed
-
- Balla, A., G. Tuymetova, A. Tsiomenko, P. Varnai, and T. Balla. 2005. A plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate is generated by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type-III alpha: studies with the PH domains of the oxysterol binding protein and FAPP1. Mol. Biol. Cell 16:1282-1295. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beatty, W. L. 2006. Trafficking from CD63-positive late endocytic multivesicular bodies is essential for intracellular development of Chlamydia trachomatis. J. Cell.Sci. 119:350-359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

