Induction of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta1-dependent predominant Th17 differentiation by group A streptococcal infection
- PMID: 20231435
- PMCID: PMC2851870
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0904831107
Induction of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta1-dependent predominant Th17 differentiation by group A streptococcal infection
Abstract
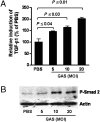
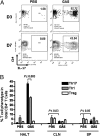
Recurrent group A Streptococcus (GAS) tonsillitis and associated autoimmune diseases indicate that the immune response to this organism can be ineffective and pathological. TGF-beta1 is recognized as an essential signal for generation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and T helper (Th) 17 cells. Here, the impact of TGF-beta1 induction on the T-cell response in mouse nasal-associated lymphoid tissue (NALT) following intranasal (i.n.) infections is investigated. ELISA and TGF-beta1-luciferase reporter assays indicated that persistent infection of mouse NALT with GAS sets the stage for TGF-beta1 and IL-6 production, signals required for promotion of a Th17 immune response. As predicted, IL-17, the Th17 signature cytokine, was induced in a TGF-beta1 signaling-dependent manner in single-cell suspensions of both human tonsils and NALT. Intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry demonstrated that CD4(+) IL-17(+) T cells are the dominant T cells induced in NALT by i.n. infections. Moreover, naive mice acquired the potential to clear GAS by adoptive transfer of CD4(+) T cells from immunized IL-17A(+)/(+) mice but not cells from IL-17A(-)/(-) mice. These experiments link specific induction of TGF-beta1 by a bacterial infection to an in vivo Th17 immune response and show that this cellular response is sufficient for protection against GAS. The association of a Th17 response with GAS infection reveals a potential mechanism for destructive autoimmune responses in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
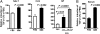
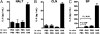
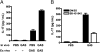
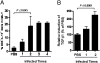

References
-
- Brook I. Penicillin failure and copathogenicity in streptococcal pharyngotonsillitis. J Fam Pract. 1994;38:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Paradise JL, et al. Tonsillectomy and adenotonsillectomy for recurrent throat infection in moderately affected children. Pediatrics. 2002;110:7–15. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham MW. Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections and their sequelae. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;609:29–42. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

