Discovery of a highly synergistic anthelmintic combination that shows mutual hypersusceptibility
- PMID: 20231450
- PMCID: PMC2851895
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912327107
Discovery of a highly synergistic anthelmintic combination that shows mutual hypersusceptibility
Abstract
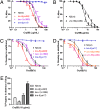
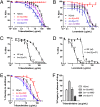
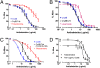
The soil-transmitted helminths or nematodes (hookworms, whipworms, and Ascaris) are roundworms that infect more than 1 billion of the poorest peoples and are leading causes of morbidity worldwide. Few anthelmintics are available for treatment, and only one is commonly used in mass drug administrations. New anthelmintics are urgently needed, and crystal (Cry) proteins made by Bacillus thuringiensis are promising new candidates. Combination drug therapies are considered the ideal treatment for infectious diseases. Surprisingly, little work has been done to define the characteristics of anthelmintic combinations. Here, by means of quantitative assays with wild-type and mutants of the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans, we establish a paradigm for studying anthelmintic combinations using Cry proteins and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) agonists, e.g., tribendimidine and levamisole. We find that nAChR agonists and Cry proteins, like Cry5B and Cry21A, mutually display what is known in the HIV field as hypersusceptibility--when the nematodes become resistant to either class, they become hypersensitive to the other class. Furthermore, we find that when Cry5B and nAChR agonists are combined, their activities are strongly synergistic, producing combination index values as good or better than seen with antitumor, anti-HIV, and insecticide combinations. Our study provides a powerful means by which anthelmintic combination therapies can be examined and demonstrate that the combination of nAChR agonists and Cry proteins has excellent properties and is predicted to give improved cure rates while being recalcitrant to the development of parasite resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
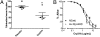
Similar articles
-
In vivo and in vitro studies of Cry5B and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist anthelmintics reveal a powerful and unique combination therapy against intestinal nematode parasites.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 May 18;12(5):e0006506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006506. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29775454 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5B protein is highly efficacious as a single-dose therapy against an intestinal roundworm infection in mice.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010 Mar 2;4(3):e614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000614. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010. PMID: 20209154 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic and single-dose in vivo therapeutic studies of Cry5B anthelmintic action against hookworms.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(11):e1900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001900. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 23145203 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial pore-forming proteins as anthelmintics.Invert Neurosci. 2012 Jun;12(1):37-41. doi: 10.1007/s10158-012-0135-8. Epub 2012 May 5. Invert Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22562659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: a comparison of the nAChRs of Caenorhabditis elegans and parasitic nematodes.Parasitol Int. 2013 Dec;62(6):606-15. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Parasitol Int. 2013. PMID: 23500392 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitazoxanide: nematicidal mode of action and drug combination studies.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2014 Jan;193(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2013.12.002. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24412397 Free PMC article.
-
The nematode (Ascaris suum) intestine is a location of synergistic anthelmintic effects of Cry5B and levamisole.PLoS Pathog. 2024 May 17;20(5):e1011835. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011835. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38758969 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating antimalarial drug interactions of emetine dihydrochloride hydrate using CalcuSyn-based interactivity calculations.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 3;12(3):e0173303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173303. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28257497 Free PMC article.
-
A new paraprobiotic-based treatment for control of Haemonchus contortus in sheep.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2020 Dec;14:230-236. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 33242790 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Drug-Drug Interaction Study of the Effects of Ivermectin and Oxantel Pamoate on Tribendimidine.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Dec 21;63(1):e00762-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00762-18. Print 2019 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30323047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bethony J, et al. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: Ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet. 2006;367:1521–1532. - PubMed
-
- Hotez PJ, et al. New technologies for the control of human hookworm infection. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Hotez PJ. Forgotten people, Forgotten diseases: The neglected tropical diseases and their impact on global health and development. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2008. pp. 13–27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

