Surgery with or without preoperative paclitaxel and carboplatin in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: Southwest Oncology Group Trial S9900, an intergroup, randomized, phase III trial
- PMID: 20231678
- PMCID: PMC2860367
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.1685
Surgery with or without preoperative paclitaxel and carboplatin in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: Southwest Oncology Group Trial S9900, an intergroup, randomized, phase III trial
Abstract
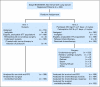
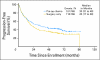
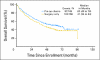
PURPOSE Patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have a poor prognosis even after complete resection. Earlier studies of preoperative (induction) chemotherapy in resectable NSCLC demonstrated feasibility and encouraging survival data. This randomized phase III trial compared overall survival (OS) for preoperative paclitaxel and carboplatin followed by surgery with surgery alone in patients with early-stage NSCLC. PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients with clinical stage IB-IIIA NSCLC (excluding superior sulcus tumors and N2 disease) were eligible. Patients were randomly assigned to surgery alone or to three cycles of paclitaxel (225 mg/m(2)) and carboplatin (area under curve, 6) followed by surgical resection. The primary end point was OS; secondary end points were progression-free survival (PFS), chemotherapy response, and toxicity. RESULTS The trial closed early with 354 patients after reports of a survival benefit for postoperative chemotherapy in other studies. The median OS was 41 months in the surgery-only arm and 62 months in the preoperative chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.60 to 1.06; P = .11.) The median PFS was 20 months for surgery alone and 33 months for preoperative chemotherapy (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.61 to 1.04; P = .10.) Major response to chemotherapy was seen in 41% of patients; no unexpected toxicity was observed. CONCLUSION This trial closed prematurely after compelling evidence supporting postoperative chemotherapy emerged. Although OS and PFS were higher with preoperative chemotherapy, the differences did not reach statistical significance. At present, stronger evidence exists for postoperative chemotherapy in early-stage NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Roth J, Fossella F, Komaki R, et al. A randomized trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy and surgery with surgery alone in resectable stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994;86:673–680. - PubMed
-
- Roth J, Atkinson E, Fossella F, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients enrolled in a randomized trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy and surgery with surgery alone in resectable stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 1998;21:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Gomez-Codina J, Camps C, et al. A randomized trial comparing preoperative chemotherapy plus surgery with surgery alone in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Gomez-Codina J, Camps C, et al. Preresectional chemotherapy in stage IIIA non-small cell lung cancer: A 7-year assessment of a randomized controlled trial. Lung Cancer. 1999;47:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Dillman R, Seagren S, Herndon J, et al. Improved survival in stage III non-small cell lung cancer: Seven-year follow-up of CALGB 8433. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996;88:1210–1215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA105409/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA086780/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA86780/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA022433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46136/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA076447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA074647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA105409/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA67663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA74647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067663/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

