Effect of the selective kappa-opioid receptor antagonist JDTic on nicotine antinociception, reward, and withdrawal in the mouse
- PMID: 20232057
- PMCID: PMC2866121
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-010-1803-1
Effect of the selective kappa-opioid receptor antagonist JDTic on nicotine antinociception, reward, and withdrawal in the mouse
Abstract
Rationale: Several lines of evidence support a role for the endogenous opioid system in mediating behaviors associated with drug dependence. Specifically, recent findings suggest that the kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) may play a role in aspects of nicotine dependence, which contribute to relapse and continued tobacco smoking.
Objective: The objective of this study is to determine the involvement of the KOR in the initial behavioral responses of nicotine, nicotine reward, and nicotine withdrawal using the highly selective KOR antagonist JDTic. JDTic doses of 1, 4, 8, or 16 mg/kg were administered subcutaneously (s.c.) 18 h prior to nicotine treatment.
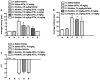
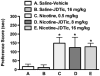
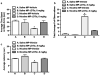
Results: JDTic dose-dependently blocked acute nicotine-induced antinociception in the tail-flick but not the hot-plate test and did not significantly attenuate morphine's antinociceptive effect in either the tail-flick or hot-plate test. Furthermore, JDTic (8 and 16 mg/kg, s.c.) failed to block the expression of nicotine reward as measured by the conditioned place preference model. In contrast, JDTic and the KOR antagonist norBNI attenuated the expression of both the physical (somatic signs and hyperalgesia) and affective (anxiety-related behavior and conditioned place aversion) nicotine withdrawal signs.
Conclusions: Our findings clearly show that the KOR is involved in mediating the withdrawal aspects of nicotine dependence. The results from this study suggest that blockade of the KOR by selective KOR antagonists may be useful smoking cessation pharmacotherapies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of orally-bioavailable short-acting kappa opioid receptor-selective antagonist LY2456302 on nicotine withdrawal in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Oct;97:270-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.05.023. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26044637 Free PMC article.
-
The kappa opioid receptor antagonist JDTic attenuates alcohol seeking and withdrawal anxiety.Addict Biol. 2012 May;17(3):634-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00455.x. Addict Biol. 2012. PMID: 22515275 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of the novel kappa opioid receptor antagonist, JDTic, on reinstatement of cocaine-seeking induced by footshock stressors vs cocaine primes and its antidepressant-like effects in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Nov;183(1):118-26. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0167-4. Epub 2005 Oct 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 16184376
-
Pharmacological properties of JDTic: a novel kappa-opioid receptor antagonist.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 6;501(1-3):111-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.08.028. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15464069
-
Behavioral Pharmacology of Novel Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists in Rats.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019 Nov 1;22(11):735-745. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz054. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31613314 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of nucleus accumbens CREB and dynorphin in dysregulation of motivation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013 Feb 1;3(2):a012005. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012005. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013. PMID: 23293139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the dynorphin/κ opioid receptor system in anxiety.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Jul;36(7):783-90. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.32. Epub 2015 May 18. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25982631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major Depressive Disorder and Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists.Transl Perioper Pain Med. 2016;1(2):4-16. Transl Perioper Pain Med. 2016. PMID: 27213169 Free PMC article.
-
Two short-acting kappa opioid receptor antagonists (zyklophin and LY2444296) exhibited different behavioral effects from the long-acting antagonist norbinaltorphimine in mouse anxiety tests.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Feb 26;615:15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26780565 Free PMC article.
-
Simple Tetrahydroisoquinolines Are Potent and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017 May 25;8(7):742-745. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00115. eCollection 2017 Jul 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28740609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bals-Kubik R, Ableitner A, Herz A, Shippenberg TS. Neuroanatomical sites mediating the motivational effects of opioids as mapped by the conditioned place preference paradigm in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Beardsley PM, Howard JL, Shelton KL, Carroll FI. Differential effects of the novel kappa opioid receptor antagonist, JDTic, on reinstatement of cocaine-seeking induced by footshock stressors vs cocaine primes and its antidepressant-like effects in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;183:118–126. - PubMed
-
- Campbell VC, Taylor RE, Tizabi Y. Effects of selective opioid receptor antagonists on alcohol-induced and nicotine-induced antinociception. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:1435–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

