The effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on prepulse inhibition and CRF-induced prepulse inhibition deficits in the rat
- PMID: 20232058
- PMCID: PMC2946822
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-010-1799-6
The effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on prepulse inhibition and CRF-induced prepulse inhibition deficits in the rat
Abstract
Rationale: Kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) agonists produce dysphoria and psychotomimesis in humans. KORs are enriched in the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions that regulate mood and cognitive function. Dysregulation of the dynorphin/KOR system has been implicated in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia, depression, and bipolar disorder. Prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex (PPI), a sensorimotor gating process, is disrupted in many psychiatric disorders.
Objectives: The present study determined whether KOR ligands alter PPI in rats.
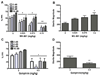
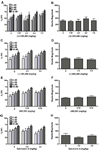
Results: Utilizing a range of doses of the synthetic KOR agonists (+/-) U50,488, (-) U50,488, and U69,593 and the naturally occurring KOR agonist, Salvinorin A, we demonstrate that KOR activation does not alter PPI or startle reactivity in rats. Similarly, selective KOR blockade using the long-acting antagonist nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) was without effect. In contrast to KOR ligands, MK-801 and quinpirole produced deficits in PPI. Stress and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) decrease PPI levels. The dynorphin/KOR system has been suggested to be a key mediator of various behavioral effects produced by stress and CRF. We therefore examined the contribution of KORs to CRF-induced alterations in PPI. Intracerebroventricular infusion of CRF decreased PPI. Administration of nor-BNI failed to affect the CRF-evoked disruption in PPI.
Conclusions: Together, these results provide no evidence of a link between the dynorphin/KOR system and deficits in sensory gating processes. Additional studies, however, examining whether dysregulation of this opioid system contributes to cognitive deficits and other behavioral abnormalities associated with psychiatric disorders are warranted.
Figures
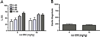

Similar articles
-
Effects of the psychotomimetic benzomorphan N-allylnormetazocine (SKF 10,047) on prepulse inhibition of startle in mice.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016 Sep;148:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 May 26. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016. PMID: 27236030 Free PMC article.
-
The role of kappa opioid receptors in stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking in rats.Brain Behav. 2014 May;4(3):356-67. doi: 10.1002/brb3.222. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Brain Behav. 2014. PMID: 24944865 Free PMC article.
-
Kappa opioid receptor activation disrupts prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats.Biol Psychiatry. 2005 Jun 15;57(12):1550-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.02.030. Biol Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15953492
-
Kappa-opioid ligands in the study and treatment of mood disorders.Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Sep;123(3):334-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.05.008. Epub 2009 Jun 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19497337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.062. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19716811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Animal models of serotonergic psychedelics.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;4(1):33-42. doi: 10.1021/cn300138m. Epub 2012 Sep 24. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23336043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynorphin/κ-opioid receptor system and its role in psychiatric disorders.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Mar;69(6):857-96. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0844-x. Epub 2011 Oct 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22002579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Feb 3;14(2):116. doi: 10.3390/ph14020116. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33546518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kappa opioid receptor signaling in the brain: Circuitry and implications for treatment.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 1;62:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25592680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A.Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Jun;63(2):316-47. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003244. Epub 2011 Mar 28. Pharmacol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21444610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armario A, Escorihuela RM, Nadal R. Long-term neuroendocrine and behavioural effects of a single exposure to stress in adult animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008;32:1121–1135. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AF. Catecholamine and second messenger influences on prefrontal cortical networks of “representational knowledge”: a rational bridge between genetics and the symptoms of mental illness. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17:6–15. - PubMed
-
- Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA. Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;271:787–794. - PubMed
-
- Bortolato M, Solbrig MV. The price of seizure control: dynorphins in interictal and postictal psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2007;151:139–143. - PubMed
-
- Bortolato M, Aru GN, Frau R, Orrù M, Fà M, Manunta M, Puddu M, Mereu G, Gessa GL. Kappa opioid receptor activation disrupts prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:1550–1558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

