Peptide heterodimers for molecular imaging
- PMID: 20232091
- PMCID: PMC3619030
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-010-0546-y
Peptide heterodimers for molecular imaging
Abstract
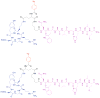
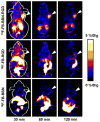
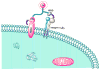
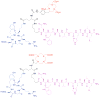
One main issue with peptide-based molecular imaging probes is their relatively low tumor affinity and short retention time. To improve peptide binding affinity, multivalency approach has been introduced. Traditionally, this approach involves the use of peptide homodimers or homomultimers in which peptide ligands of the same type are constructed with suitable linkers. Recently, a new approach using peptide heterodimers has emerged as a promising method for targeting multi-receptor over-expressed tumor cells. Significant affinity enhancements have been observed with peptide heterodimers compared with their parent peptide monomers. In a peptide heterodimer, two different peptide ligands capable of targeting two different receptors are covalently linked. The binding modes of peptide heterodimers can be monovalent or bivalent depending on whether simultaneous binding of two ligands can be achieved. Increased local ligand concentration and improved binding kinetics contribute to enhanced binding in both monovalent- and bivalent binding modes, while multivalency effect also plays an important role in bivalent binding mode. As many tumors overexpress multiple receptors, more peptide heterodimer-based molecular imaging probes are expected to be developed in future. This review article will discuss the peptide homodimers and heterodimers for molecular imaging with special emphasis on peptide heterodimers.
Figures
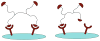

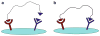
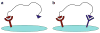
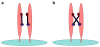




References
-
- Aloj L, Morelli G. Design, synthesis and preclinical evaluation of radiolabeled peptides for diagnosis and therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:3009–3031. - PubMed
-
- Benedetti E, Morelli G, Accardo A, Mansi R, Tesauro D, Aloj L. Criteria for the design and biological characterization of radiolabeled peptide-based pharmaceuticals. BioDrugs. 2004;18:279–295. - PubMed
-
- Handl HL, Vagner J, Han H, Mash E, Hruby VJ, Gillies RJ. Hitting multiple targets with multimeric ligands. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2004;8:565–586. - PubMed
-
- Kwekkeboom D, Krenning EP, de Jong M. Peptide receptor imaging and therapy. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1704–1713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

