Protein-based tumor molecular imaging probes
- PMID: 20232092
- PMCID: PMC3617487
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-010-0545-z
Protein-based tumor molecular imaging probes
Abstract
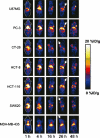
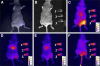
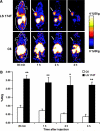
Molecular imaging is an emerging discipline which plays critical roles in diagnosis and therapeutics. It visualizes and quantifies markers that are aberrantly expressed during the disease origin and development. Protein molecules remain to be one major class of imaging probes, and the option has been widely diversified due to the recent advances in protein engineering techniques. Antibodies are part of the immunosystem which interact with target antigens with high specificity and affinity. They have long been investigated as imaging probes and were coupled with imaging motifs such as radioisotopes for that purpose. However, the relatively large size of antibodies leads to a half-life that is too long for common imaging purposes. Besides, it may also cause a poor tissue penetration rate and thus compromise some medical applications. It is under this context that various engineered protein probes, essentially antibody fragments, protein scaffolds, and natural ligands have been developed. Compared to intact antibodies, they possess more compact size, shorter clearance time, and better tumor penetration. One major challenge of using protein probes in molecular imaging is the affected biological activity resulted from random labeling. Site-specific modification, however, allows conjugation happening in a stoichiometric fashion with little perturbation of protein activity. The present review will discuss protein-based probes with focus on their application and related site-specific conjugation strategies in tumor imaging.
Figures
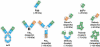

Similar articles
-
Protein and peptide probes for molecular imaging.Amino Acids. 2011 Nov;41(5):1009-12. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-0945-8. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 21643775 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protein scaffold-based molecular probes for cancer molecular imaging.Amino Acids. 2011 Nov;41(5):1037-47. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0503-9. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20174842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical and multimodal peptide-based probes for in vivo molecular imaging.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Jun;12(5):476-99. doi: 10.2174/187152012800617858. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22292759 Review.
-
ADAPT, a Novel Scaffold Protein-Based Probe for Radionuclide Imaging of Molecular Targets That Are Expressed in Disseminated Cancers.Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;75(20):4364-71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3497. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26297736
-
Peptide heterodimers for molecular imaging.Amino Acids. 2011 Nov;41(5):1081-92. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0546-y. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20232091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Axl and EGFR Dual-Specific Binding Affibody for Targeted Therapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Cells. 2024 Nov 5;13(22):1823. doi: 10.3390/cells13221823. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594573 Free PMC article.
-
Protein and peptide probes for molecular imaging.Amino Acids. 2011 Nov;41(5):1009-12. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-0945-8. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 21643775 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Characterization of human colorectal cancer MDR1/P-gp Fab antibody.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Nov 7;2013:716289. doi: 10.1155/2013/716289. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24348182 Free PMC article.
-
EphB4-targeted imaging with antibody h131, h131-F(ab')2 and h131-Fab.Mol Pharm. 2013 Dec 2;10(12):4527-33. doi: 10.1021/mp400354y. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24147882 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging of glioblastoma multiforme using anti-insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 single-domain antibodies.Br J Cancer. 2010 Nov 9;103(10):1606-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605937. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Br J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20959824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel-Santos E, Scott CP, Benkovic SJ. Use of inteins for the in vivo production of stable cyclic peptide libraries in E coli. Methods Mol Biol. 2003;205:281–294. - PubMed
-
- Adams GP, Schier R. Generating improved single-chain Fv molecules for tumor targeting. J Immunol Methods. 1999;231(1–2):249–260. - PubMed
-
- Adams GP, McCartney JE, Tai MS, et al. Highly specific in vivo tumor targeting by monovalent and divalent forms of 741F8 anti-c-erbB-2 single-chain Fv. Cancer Res. 1993;53(17):4026–4034. - PubMed
-
- Allan SM, Dean CJ, Eccles S, Sacks NP. Clinical radioimmunolocalization with a rat monoclonal antibody directed against c-erbB-2. Cell Biophys. 1994;24–25:93–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

