C-Myc is a Nrf2-interacting protein that negatively regulates phase II genes through their electrophile responsive elements
- PMID: 20232342
- PMCID: PMC2852429
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.314
C-Myc is a Nrf2-interacting protein that negatively regulates phase II genes through their electrophile responsive elements
Abstract
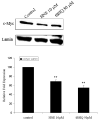
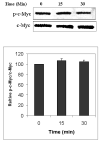
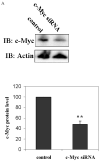
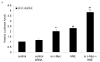
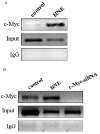
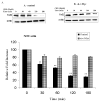
c-Myc is a transcription factor that is implicated in many cellular processes including proliferation, apoptosis and cancers. Recently, c-Myc was shown to be involved in regulation of glutamate cysteine ligase through E-box sequences. This investigation examined whether c-Myc also regulates phase II genes through interaction with the electrophile response element (EpRE). Experiments were conducted in human bronchial epithelial cells using si-RNA to knock down c-Myc. RT-PCR and reporter assays were used to measure transcription and promoter activity. c-Myc downregulated transcription and promoter activity of phase II genes. Chromatin immunoprecipitation verified binding of c-Myc to EpRE while coimmunoprecipitation demonstrated interaction of c-Myc with Nrf2. c-Myc also forms a ternary complex with Nrf2 and p-c-Jun. Finally, c-Myc decreased Nrf2 stability. Thus, our results suggest regulation of the EpRE/Nrf2 signaling pathway by c-Myc through both interaction with the EpRE binding complex and increased degradation of Nrf2.
2010 IUBMB
Figures








References
-
- Nilsson JA, Cleveland JL. Myc pathways provoking cell suicide and cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22(56):9007–9021. - PubMed
-
- Nesbit CE, Tersak JM, Prochownik EV. MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 1999;18(19):3004–3016. - PubMed
-
- Dang CV, Resar LM, Emison E, Kim S, Li Q, Prescott JE, Wonsey D, Zeller K. Function of the c-Myc oncogenic transcription factor. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253(1):63–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

