In vivo matrix metalloproteinase-7 substrates identified in the left ventricle post-myocardial infarction using proteomics
- PMID: 20232908
- PMCID: PMC2866015
- DOI: 10.1021/pr100147r
In vivo matrix metalloproteinase-7 substrates identified in the left ventricle post-myocardial infarction using proteomics
Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) deletion has been shown to improve survival after myocardial infarction (MI). MMP-7 has a large array of in vitro substrates, but in vivo substrates for MMP-7 following MI have not been fully identified. Accordingly, we evaluated the infarct regions of wild-type (WT; n = 12) and MMP-7 null (null; n = 10) mice using a proteomic strategy. Seven days post-MI, infarct regions of the left ventricles were excised, homogenized, and protein extracts were analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Of 13 spots that showed intensity differences between WT and null, the intensities of eight spots were higher and those of five spots were lower in the null group (p < 0.05). Fibronectin and tenascin-C, known in vitro substrates of MMP-7, were identified in spots that showed lower intensity in the null. Immunoblotting and in vitro cleavage assays confirmed reduced fibronectin and tenascin-C fragment generation in the null, and this effect was restored by exogenous administration of MMP-7. Lower levels of full-length peroxiredoxin-1 and -2 and higher levels of the full-length peroxiredoxin-3 were detected in the null group, suggesting MMP-7 deletion may also indirectly regulate protein levels through nonenzymatic mechanisms. In conclusion, this is the first study to identify fibronectin and tenascin-C as in vivo MMP-7 substrates in the infarcted left ventricle using a proteomic approach.
Figures
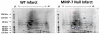
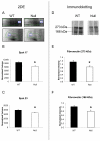

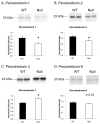
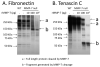

References
-
- Crabbe T, Willenbrock F, Eaton D, Hynds P, Carne AF, Murphy G, Docherty AJ. Biochemical characterization of matrilysin. Activation conforms to the stepwise mechanisms proposed for other matrix metalloproteinases. Biochemistry. 1992;31(36):8500–7. - PubMed
-
- Gaire M, Magbanua Z, McDonnell S, McNeil L, Lovett DH, Matrisian LM. Structure and expression of the human gene for the matrix metalloproteinase matrilysin. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(3):2032–40. - PubMed
-
- Boixel C, Fontaine V, Rucker-Martin C, Milliez P, Louedec L, Michel JB, Jacob MP, Hatem SN. Fibrosis of the left atria during progression of heart failure is associated with increased matrix metalloproteinases in the rat. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(2):336–44. - PubMed
-
- Furman C, Copin C, Kandoussi M, Davidson R, Moreau M, McTaggiart F, Chapman MJ, Fruchart J-C, Rouis M. Rosuvastatin reduces MMP-7 secretion by human monocyte-derived macrophages: potential relevance to atherosclerotic plaque stability. Atherosclerosis. 2004;174(1):93–98. - PubMed
-
- Lindsey ML, Escobar GP, Mukherjee R, Goshorn DK, Sheats NJ, Bruce JA, Mains IM, Hendrick JK, Hewett KW, Gourdie RG, Matrisian LM, Spinale FG. Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Affects Connexin-43 Levels, Electrical Conduction, and Survival After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2006;113(25):2919–2928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

