Inverse agonist and neutral antagonist actions of synthetic compounds at an insect 5-HT1 receptor
- PMID: 20233210
- PMCID: PMC2850402
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00638.x
Inverse agonist and neutral antagonist actions of synthetic compounds at an insect 5-HT1 receptor
Abstract
Background and purpose: 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) has been shown to control and modulate many physiological and behavioural functions in insects. In this study, we report the cloning and pharmacological properties of a 5-HT(1) receptor of an insect model for neurobiology, physiology and pharmacology.
Experimental approach: A cDNA encoding for the Periplaneta americana 5-HT(1) receptor was amplified from brain cDNA. The receptor was stably expressed in HEK 293 cells, and the functional and pharmacological properties were determined in cAMP assays. Receptor distribution was investigated by RT-PCR and by immunocytochemistry using an affinity-purified polyclonal antiserum.
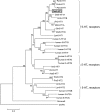
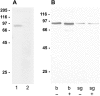
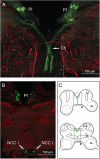
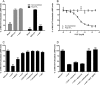
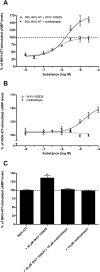
Key results: The P. americana 5-HT(1) receptor (Pea5-HT(1)) shares pronounced sequence and functional similarity with mammalian 5-HT(1) receptors. Activation with 5-HT reduced adenylyl cyclase activity in a dose-dependent manner. Pea5-HT(1) was expressed as a constitutively active receptor with methiothepin acting as a neutral antagonist, and WAY 100635 as an inverse agonist. Receptor mRNA was present in various tissues including brain, salivary glands and midgut. Receptor-specific antibodies showed that the native protein was expressed in a glycosylated form in membrane samples of brain and salivary glands.
Conclusions and implications: This study marks the first pharmacological identification of an inverse agonist and a neutral antagonist at an insect 5-HT(1) receptor. The results presented here should facilitate further analyses of 5-HT(1) receptors in mediating central and peripheral effects of 5-HT in insects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
5-HT1 receptors.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Feb;3(1):1-10. doi: 10.2174/1568007043482570. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 14965240 Review.
-
Molecular characterization and localization of the first tyramine receptor of the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana).Neuroscience. 2009 Sep 15;162(4):1120-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.066. Epub 2009 May 29. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19482069
-
Molecular cloning, pharmacological properties and tissue distribution of the porcine 5-HT(1B) receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jul;133(6):891-901. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704150. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11454663 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological characterization of a 5-HT1-type serotonin receptor in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e65052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065052. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741451 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of serotonin-induced salivary secretion in Periplaneta americana.J Insect Physiol. 2007 Aug;53(8):774-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2007.02.020. Epub 2007 Mar 18. J Insect Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17475273
Cited by
-
Insulin-producing cells in the brain of adult Drosophila are regulated by the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Feb;69(3):471-84. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0789-0. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 21818550 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Pharmacological Characterization of Two Serotonin Type 7 Receptor Isoforms from Mythimna separata.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):655. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010655. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614100 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Biogenic Amine Receptor Types Modulate Spider, Cupiennius salei, Mechanosensory Neurons.Front Physiol. 2018 Jul 9;9:857. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00857. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30050453 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and pharmacological characterization of serotonin 5-HT2α and 5-HT7 receptors in the salivary glands of the blowfly Calliphora vicina.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049459. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23145175 Free PMC article.
-
AmOctα2R: Functional Characterization of a Honeybee Octopamine Receptor Inhibiting Adenylyl Cyclase Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 8;21(24):9334. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249334. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33302363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anstey ML, Rogers SM, Ott SR, Burrows M, Simpson SJ. 5-HT mediates behavioral gregarization underlying swarm formation in desert locusts. Science. 2009;323:627–630. - PubMed
-
- Barbas D, Zappulla JP, Angers S, Bouvier M, Castellucci VF, DesGroseillers L. Functional characterization of a novel 5-HT receptor (5-HTap2) expressed in the CNS of Aplysia californica. J Neurochem. 2002;80:335–345. - PubMed
-
- Beggs KT, Hamilton IS, Kurshan PT, Mustard JA, Mercer AR. Characterization of a D2-like dopamine receptor (AmDOP3) in honey bee, Apis mellifera. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;35:873–882. - PubMed
-
- Bell WJ, Sams GR. Aggressiveness in the cockroach Periplaneta americana (Orthoptera, Blattidae) Behav Biol. 1973;9:581–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

