Atherosclerosis induced by chronic inhibition of the synthesis of nitric oxide in moderately hypercholesterolaemic rabbits is suppressed by pitavastatin
- PMID: 20233214
- PMCID: PMC2850399
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00630.x
Atherosclerosis induced by chronic inhibition of the synthesis of nitric oxide in moderately hypercholesterolaemic rabbits is suppressed by pitavastatin
Abstract
Background and purpose: It is not clear if the new 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor pitavastatin prevents atherogenesis by a direct effect. Statins have a cholesterol-lowering effect, so an accessible animal model of atherosclerosis showing only moderate hypercholesterolaemia as in humans, is needed. The effects of pitavastatin were evaluated on atherosclerotic lesions accumulating foam cells derived from macrophages, produced in rabbits with moderate hypercholesterolaemia by chronic inhibition of nitric oxide synthase (NOS).
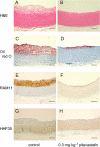
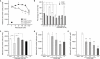
Experimental approach: White New Zealand rabbits were fed a 0.2% cholesterol diet with the NOS inhibitor N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) in the same diet. Pitavastatin (0.1 and 0.3 mg x kg(-1)) was given orally once a day for 8 weeks. The aortic arch and thoracic aorta were analysed by histochemistry and atherosclerotic lesions were quantified. The effect of pitavastatin on adhesion of THP-1 cells to endothelial cells, and cholesterol content in RAW264.7 cells incubated with oxidized or acetylated LDL were also investigated.
Key results: Atherosclerotic lesions containing foam cells were induced in a model of atherosclerosis in rabbits with moderate hypercholesterolaemia by chronic inhibition of NOS. The area of atherosclerotic lesions was diminished by pitavastatin administration. The adhesion of THP-1 cells and cholesteryl ester content in RAW macrophages were decreased by pitavastatin treatment.
Conclusion: Atherosclerosis induced by chronic inhibition of NOS in moderately hypercholesterolaemic rabbits was suppressed by pitavastatin via inhibition of macrophage accumulation and macrophage foam cell formation.
Figures


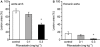
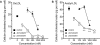

References
-
- Aikawa M, Rabkin E, Okada Y, Voglic SJ, Clinton SK, Brinckerhoff CE, et al. Lipid lowering by diet reduces matrix metalloproteinase activity and increases collagen content of rabbit atheroma: a potential mechanism of lesion stabilization. Circulation. 1998;97:2433–2444. - PubMed
-
- Alegret M, Silvestre JS. Pleiotropic effects of statins and related pharmacological experimental approaches. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2006;28:627–656. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Nishimura H, Nakagawa S, Kojima J, Suzuki H, Tamaki T, et al. Pharmacological profile of a novel synthetic inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Arzneimittelforschung. 1997;47:904–909. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Yoshinaka Y, Yamazaki H, Suzuki H, Tamaki T, Sato F, et al. Triglyceride-lowering effect of pitavastatin [corrected] in a rat model of postprandial lipemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;444:107–113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

