Spinal and peripheral analgesic effects of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist AM1241 in two models of bone cancer-induced pain
- PMID: 20233215
- PMCID: PMC2931557
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00629.x
Spinal and peripheral analgesic effects of the CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist AM1241 in two models of bone cancer-induced pain
Abstract
Background and purpose: The activation of CB(2) receptors induces analgesia in experimental models of chronic pain. The present experiments were designed to study whether the activation of peripheral or spinal CB(2) receptors relieves thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in two models of bone cancer pain.
Experimental approach: NCTC 2472 osteosarcoma or B16-F10 melanoma cells were intratibially inoculated to C3H/He and C57BL/6 mice. Thermal hyperalgesia was assessed by the unilateral hot plate test and mechanical allodynia by the von Frey test. AM1241 (CB(2) receptor agonist), AM251 (CB(1) receptor antagonist), SR144528 (CB(2) receptor antagonist) and naloxone were used. CB(2) receptor expression was measured by Western blot.
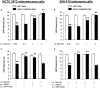
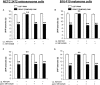
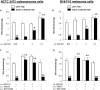
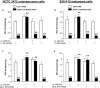
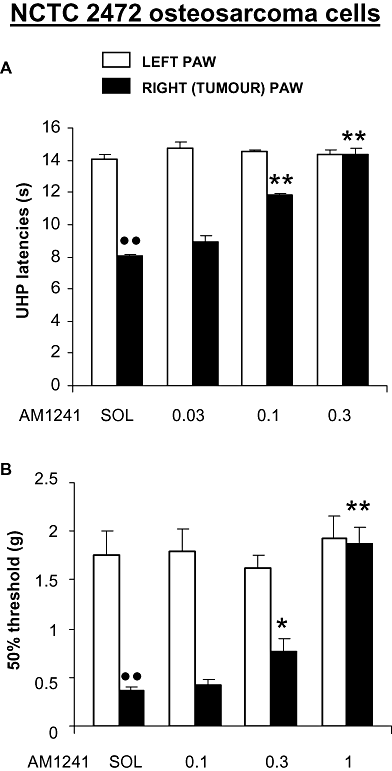
Key results: AM1241 (0.3-10 mg.kg(-1)) abolished thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in both tumour models. The antihyperalgesic effect was antagonized by subcutaneous, intrathecal or peri-tumour administration of SR144528. In contrast, the antiallodynic effect was inhibited by systemic or intrathecal, but not peri-tumour, injection of SR144528. The effects of AM1241 were unchanged by AM251 but were prevented by naloxone. No change in CB(2) receptor expression was found in spinal cord or dorsal root ganglia.
Conclusions and implications: Spinal CB(2) receptors are involved in the antiallodynic effect induced by AM1241 in two neoplastic models while peripheral and spinal receptors participate in the antihyperalgesic effects. Both effects were mediated by endogenous opiates. The use of drugs that activate CB(2) receptors could be a useful strategy to counteract bone cancer-induced pain symptoms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antinociceptive effects induced through the stimulation of spinal cannabinoid type 2 receptors in chronically inflamed mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 1;668(1-2):184-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.06.057. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21771590
-
Selective activation of cannabinoid CB(2) receptors suppresses spinal fos protein expression and pain behavior in a rat model of inflammation.Neuroscience. 2003;119(3):747-57. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00126-x. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12809695
-
Interaction of a Cannabinoid-2 Agonist With Tramadol on Nociceptive Thresholds and Immune Responses in a Rat Model of Incisional Pain.Am J Ther. 2016 Nov/Dec;23(6):e1484-e1492. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000131. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 25370921
-
[The cannabinoid system and pain: towards new drugs?].J Soc Biol. 2009;203(1):99-106. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2009002. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Soc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19358815 Review. French.
-
Cannabinoid receptors and pain.Prog Neurobiol. 2001 Apr;63(5):569-611. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(00)00031-9. Prog Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11164622 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic changes to the endocannabinoid system in models of chronic pain.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Dec 5;367(1607):3300-11. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0390. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23108548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal effects of chronic pharmacological manipulation of CB2 receptors in rats with diet-induced obesity.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;173(7):1128-42. doi: 10.1111/bph.13056. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 25537025 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral versus central mechanisms of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor agonist AM1710 in a mouse model of neuropathic pain.Brain Behav. 2020 Dec;10(12):e01850. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1850. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 32977358 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of breast cancer cell viability by a cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist, JWH-015, is calcium dependent.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2016 Apr 15;8:59-71. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S100393. eCollection 2016. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2016. PMID: 27186076 Free PMC article.
-
The Endocannabinoid/Endovanilloid System in Bone: From Osteoporosis to Osteosarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 18;20(8):1919. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081919. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31003519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anand U, Otto WR, Sanchez-Herrera D, Facer P, Yiangou Y, Korchev Y, et al. Cannabinoid receptor CB2 localisation and agonist-mediated inhibition of capsaicin responses in human sensory neurons. Pain. 2008;138:667–680. - PubMed
-
- Baamonde A, Curto-Reyes V, Juárez L, Meana A, Hidalgo A, Menéndez L. Antihyperalgesic effects induced by the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra and increased IL-1beta levels in inflamed and osteosarcoma-bearing mice. Life Sci. 2007;81:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Baamonde A, Lastra A, Juárez L, García V, Hidalgo A, Menéndez L. Effects of the local administration of selective mu-, delta-and kappa-opioid receptor agonists on osteosarcoma-induced hyperalgesia. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005;372:213–219. - PubMed
-
- Baamonde A, Lastra A, Juárez L, García-Suárez O, Meana A, Hidalgo A, et al. Endogenous beta-endorphin induces thermal analgesia at the initial stages of a murine osteosarcoma. Peptides. 2006;27:2778–2785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

