Pioglitazone improves lipid and insulin levels in overweight rats on a high cholesterol and fructose diet by decreasing hepatic inflammation
- PMID: 20233219
- PMCID: PMC2958635
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00671.x
Pioglitazone improves lipid and insulin levels in overweight rats on a high cholesterol and fructose diet by decreasing hepatic inflammation
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: Pioglitazone Improves Lipid and Insulin Levels in Overweight Rats on a High Cholesterol and Fructose Diet by Decreasing Hepatic Inflammation.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;181(17):3300. doi: 10.1111/bph.16498. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38932505 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Nutrient overload leads to obesity and insulin resistance. Pioglitazone, a selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)gamma agonist, is currently used to manage insulin resistance, but the specific molecular mechanisms activated by PPARgamma are not yet fully understood. Recent studies suggest the involvement of suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS)-3 in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. This study aimed to investigate the hepatic signalling pathway activated by PPARgamma activation in a non-genetic insulin-resistant animal model.
Experimental approach: Male Wistar rats were maintained on a high-cholesterol fructose (HCF) diet for 15 weeks. Pioglitazone (3 mg x kg(-1)) was administered orally for the last 4 weeks of this diet. At the end of the treatment, serum was collected for biochemical analysis. Levels of PPARgamma, SOCS-3, pro-inflammatory markers, insulin receptor substrate-2 and Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylation were assessed in rat liver.
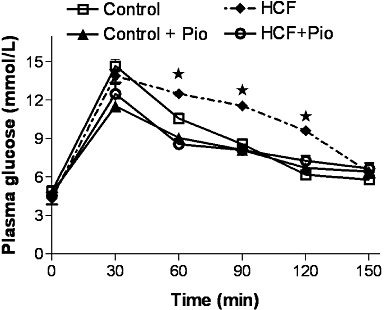
Key results: Rats fed the HCF diet exhibited hyperlipidemia, hyperinsulinemia, impaired glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. Pioglitazone administration evoked a significant improvement in lipid metabolism and insulin responsiveness. This was accompanied by reduced hepatic expression of SOCS-3, interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and markers of neutrophil infiltration. Diet-induced PPARgamma expression was unaffected by the pioglitazone treatment.
Conclusion and implications: Chronic pioglitazone administration reduced hepatic inflammatory responses in rats fed a HCF diet. These effects were associated with changes in hepatic expression of SOCS-3, which may be a crucial link between the reduced local inflammation and the improved insulin signalling.
Figures




Comment in
-
Hepatic inflammation and insulin resistance in pre-diabetes - further evidence for the beneficial actions of PPAR-gamma agonists and a role for SOCS-3 modulation.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;160(8):1889-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00739.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20649587 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Hepatic inflammation and insulin resistance in pre-diabetes - further evidence for the beneficial actions of PPAR-gamma agonists and a role for SOCS-3 modulation.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;160(8):1889-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00739.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20649587 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone normalizes insulin signaling in the diabetic rat retina through reduction in tumor necrosis factor α and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 19;289(38):26395-26405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.583880. Epub 2014 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25086044 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone can ameliorate insulin resistance in low-dose streptozotocin and high sucrose-fat diet induced obese rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005 May;26(5):575-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00090.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005. PMID: 15842776
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) agonists on glycemic control, lipid profile and cardiovascular risk.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;5(2):272-81. doi: 10.2174/1874467211205020272. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22122457 Review.
-
PPAR Gamma Receptor: A Novel Target to Improve Morbidity in Preterm Babies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 27;16(11):1530. doi: 10.3390/ph16111530. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and regulation of facilitative glucose transporters in equine insulin-sensitive tissue: from physiology to pathology.ISRN Vet Sci. 2014 Mar 4;2014:409547. doi: 10.1155/2014/409547. eCollection 2014. ISRN Vet Sci. 2014. PMID: 24977043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic syndrome: is equine disease comparable to what we know in humans?Endocr Connect. 2014 Sep;3(3):R81-93. doi: 10.1530/EC-14-0038. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Endocr Connect. 2014. PMID: 24894908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of High-Fructose Corn Syrup Addition to Broiler Diets on Performance, Carcass Yield, Visceral Weights, Gut pH and Some Blood Parameters.Vet Med Sci. 2024 Nov;10(6):e70058. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70058. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39324875 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory landscape of AGE-RAGE-oxidative stress axis and its modulation by PPARγ activation in high fructose diet-induced metabolic syndrome.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2017 Jan 13;14:5. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0149-z. eCollection 2017. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28101123 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone attenuates prostatic enlargement in diet-induced insulin-resistant rats by altering lipid distribution and hyperinsulinaemia.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Dec;161(8):1708-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00994.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20726985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anai M, Funaki M, Ogihara T, Terasaki J, Inukai K, Katagiri H, et al. Altered expression levels and impaired steps in the pathway to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation via insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 in Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes. 1998;47:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama T, Ikejima K, Kon K, Okumura K, Arai K, Watanabe S. Pioglitazone promotes survival and prevents hepatic regeneration failure after partial hepatectomy in obese and diabetic KK-A(y) mice. Hepatology. 2009;49:1636–1644. - PubMed
-
- Aragno M, Tomasinelli CE, Vercellinatto I, Catalano MG, Collino M, Fantozzi R, et al. SREBP-1c in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by Western-type high-fat diet plus fructose in rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009;47:1067–1074. - PubMed
-
- Axen KV, Dikeakos A, Sclafani A. High dietary fat promotes syndrome X in nonobese rats. J Nutr. 2003;133:2244–2249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

