Activation of submucosal 5-HT(3) receptors elicits a somatostatin-dependent inhibition of ion secretion in rat colon
- PMID: 20233224
- PMCID: PMC2925486
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00653.x
Activation of submucosal 5-HT(3) receptors elicits a somatostatin-dependent inhibition of ion secretion in rat colon
Abstract
Background and purpose: 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a key regulator of the gastrointestinal system and we have shown that submucosal neuronal 5-HT(3) receptors exerted a novel inhibitory effect on colonic ion transport. The aim of the present study was to investigate the precise mechanism(s) underlying this inhibitory effect.
Experimental approach: Mucosa/submucosa or mucosa-only preparations from rat distal colon were mounted in Ussing chambers for measurement of short-circuit current (I(sc)) as an indicator of ion secretion. Somatostatin release was determined with radioimmunoassay. Intracellular cAMP content was measured with enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay (elisa). Immunohistochemical techniques were used to study the expression of 5-HT(3) receptors, somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in colonic tissue.
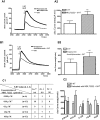
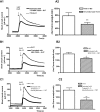
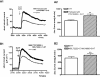
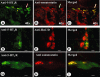
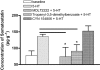
Key results: In rat distal colonic mucosa/submucosa preparations, pretreatment with 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists enhanced 5-HT-induced increases in I(sc). However, in mucosa-only preparations without retained neural elements, pretreatment with 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists inhibited 5-HT-induced DeltaI(sc). Pretreatment with a somatostatin-2 (sst(2)) receptor antagonist in mucosa/submucosa preparations augmented 5-HT-induced DeltaI(sc). Combination of sst(2) and 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists did not cause further enhancement of 5-HT-induced DeltaI(sc). Moreover, both sst(2) and 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists enhanced 5-HT-induced increase in intracellular cAMP concentration in the mucosa/submucosa preparations. 5-HT released somatostatin from rat colonic mucosa/submucosa preparations, an effect prevented by pretreatment with 5-HT(3) receptor antagonists. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated the presence of 5-HT(3) receptors on submucosal somatostatin neurons and of sst(2) receptors on colonic mucosa.
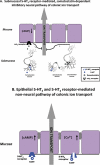
Conclusion and implications: Activation of neuronal 5-HT(3) receptors in the submucosal plexus of rat colon suppressed 5-HT-induced ion secretion by releasing somatostatin from submucosal neurons.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A dual role of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3 in serotonin induced ion transport in rat distal colon.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 14;584(1):137-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.01.027. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18313044
-
Colonic submucosal 5-HT(3) receptor-mediated somatostatin-dependent secretoinhibitory pathway is suppressed in water-immersion restraint stressed rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 10;656(1-3):94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.01.026. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21291881
-
A nonneuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3 induces chloride secretion in the rat distal colonic mucosa.Am J Surg. 2005 Nov;190(5):736-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.07.012. Am J Surg. 2005. PMID: 16226950
-
Review article: serotonin receptors and transporters -- roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Nov;20 Suppl 7:3-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02180.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15521849 Review.
-
Recent developments in 5-HT3 receptor pharmacology.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Feb;34(2):100-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.12.002. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23380247 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of entacapone on colon motility and ion transport in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar 28;21(12):3509-18. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3509. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25834315 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin regulates NHE8 protein expression via the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway in DSS-induced colitis mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):G954-G963. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00239.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27686614 Free PMC article.
-
Enteroendocrine and neuronal mechanisms in pathophysiology of acute infectious diarrhea.Dig Dis Sci. 2012 Jan;57(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1939-9. Epub 2011 Oct 15. Dig Dis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22001941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Luminal 5-HT stimulates colonic bicarbonate secretion in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;172(19):4655-70. doi: 10.1111/bph.13216. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26061462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell D, Zhao Y, McMaster B, McHenry EM, Wang X, Kelso EJ, et al. SRIF receptor subtype expression and involvement in positive and negative contractile effects of somatostatin-14 (SRIF-14) in ventricular cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2008;22:653–664. - PubMed
-
- Booth CE, Kirkup AJ, Hicks GA, Humphrey PP, Grundy D. Somatostatin sst(2) receptor-mediated inhibition of mesenteric afferent nerves of the jejunum in the anesthetized rat. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:358–369. - PubMed
-
- Budhoo MR, Kellum JM. Evidence for a 5-HT4 receptor pathway mediating chloride secretion in the rat distal colon. J Surg Res. 1994;57:44–48. - PubMed
-
- Budhoo MR, Harris RP, Kellum JM. 5-Hydroxytryptamine-induced Cl- transport is mediated by 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors in the rat distal colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 1996;298:137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

