Expression and distribution of SIBLING proteins in the predentin/dentin and mandible of hyp mice
- PMID: 20233318
- PMCID: PMC2903660
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2010.01656.x
Expression and distribution of SIBLING proteins in the predentin/dentin and mandible of hyp mice
Abstract
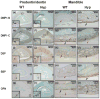
Objectives: Human X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) and its murine homologue, Hyp are caused by inactivating mutations in PHEX gene. The protein encoded by PHEX gene is an endopeptidase whose physiological substrate(s) has not been identified. Dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1) and dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP), two members of the Small Integrin-Binding LIgand, N-linked Glycoprotein (SIBLING) family are proteolytically processed. It has been speculated that PHEX endopeptidase may be responsible for the proteolytic cleavage of DMP1 and DSPP. To test this hypothesis and to analyse the distribution of SIBLING proteins in the predentin/dentin complex and mandible of Hyp mice, we compared the expression of four SIBLING proteins, DMP1, DSPP, bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteopontin (OPN) between Hyp and wild-type mice.
Methods: These SIBLING proteins were analysed by protein chemistry and immunohistochemistry.
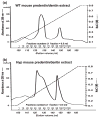
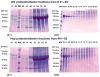
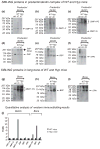
Results: (1) Dentin matrix protein 1 and DSPP fragments are present in the extracts of Hyp predentin/dentin and bone; (2) the level of DMP1 proteoglycan form, BSP and OPN is elevated in the Hyp bone.
Conclusions: The PHEX protein is not the enzyme responsible for the proteolytic processing of DMP1 and DSPP. The altered distribution of SIBLING proteins may be involved in the pathogenesis of bone and dentin defects in Hyp and XLH.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteolytic processing of osteopontin by PHEX and accumulation of osteopontin fragments in Hyp mouse bone, the murine model of X-linked hypophosphatemia.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Mar;28(3):688-99. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1766. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 22991293
-
Distribution of small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLING) in the condylar cartilage of rat mandible.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Mar;39(3):272-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.12.017. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20097540 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of sibling proteins and their roles in osteogenesis and dentinogenesis.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004 Jun 4;15(3):126-36. doi: 10.1177/154411130401500302. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15187031 Review.
-
Aberrant cementum phenotype associated with the hypophosphatemic hyp mouse.J Periodontol. 2009 Aug;80(8):1348-54. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090129. J Periodontol. 2009. PMID: 19656036 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of bone-renal mineral and energy metabolism: the PHEX, FGF23, DMP1, MEPE ASARM pathway.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2012;22(1):61-86. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v22.i1.50. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2012. PMID: 22339660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycosylation of Dentin Matrix Protein 1 is critical for osteogenesis.Sci Rep. 2015 Dec 4;5:17518. doi: 10.1038/srep17518. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26634432 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization of DMP1 proteins suggests a role in intracellular signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Aug 3;424(3):641-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.037. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22813642 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted Protein Expression and Altered Proteolytic Events in Hypophosphatemic Dentin Can Be Rescued by Dentin Matrix Protein 1.Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 14;11:82. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00082. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32116788 Free PMC article.
-
PHEXL222P Mutation Increases Phex Expression in a New ENU Mouse Model for XLH Disease.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 28;13(8):1356. doi: 10.3390/genes13081356. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011266 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Active Vitamin D or FGF23 Antibody on Hyp Mice Dentoalveolar Tissues.J Dent Res. 2021 Dec;100(13):1482-1491. doi: 10.1177/00220345211011041. Epub 2021 Apr 27. J Dent Res. 2021. PMID: 33906518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K, Ooshima T, Tong SML, Yasufuku Y, Sobue S. Structural deformities of deciduous dentin in patients with hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1988;65:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Abe K, Ooshima T, Masatomi Y, Sobue S, Moriwaki Y. Microscopic and crystallographic examinations of the dentin of the X-linked hypophosphatemic mouse. J Dent Res. 1989;68:1519–1524. - PubMed
-
- Baba O, Qin C, Brunn JC, et al. Detection of dentin sialoprotein in rat periodontium. Eur J Oral Sci. 2004a;112:163–170. - PubMed
-
- Baba O, Qin C, Brunn JC, Wygant JN, Mcintyre BW, Butler WT. Colocalization of dentin matrix protein 1 and dentin sialoprotein at late stages of rat molar development. Matrix Biol. 2004b;23:371–379. - PubMed
-
- Baroncelli GI, Angiolini M, Ninni E, Galli V, Saggese R, Giuca MR. Prevalence and pathogenesis of dental and periodontal lesions in children with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2006;7:61–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

