Characterization of the ovine ribosomal protein SA gene and its pseudogenes
- PMID: 20233419
- PMCID: PMC2850357
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-179
Characterization of the ovine ribosomal protein SA gene and its pseudogenes
Abstract
Background: The ribosomal protein SA (RPSA), previously named 37-kDa laminin receptor precursor/67-kDa laminin receptor (LRP/LR) is a multifunctional protein that plays a role in a number of pathological processes, such as cancer and prion diseases. In all investigated species, RPSA is a member of a multicopy gene family consisting of one full length functional gene and several pseudogenes. Therefore, for studies on RPSA related pathways/pathologies, it is important to characterize the whole family and to address the possible function of the other RPSA family members. The present work aims at deciphering the RPSA family in sheep.
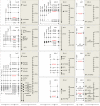
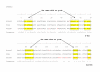
Results: In addition to the full length functional ovine RPSA gene, 11 other members of this multicopy gene family, all processed pseudogenes, were identified. Comparison between the RPSA transcript and these pseudogenes shows a large variety in sequence identities ranging from 99% to 74%. Only one of the 11 pseudogenes, i.e. RPSAP7, shares the same open reading frame (ORF) of 295 amino acids with the RPSA gene, differing in only one amino acid. All members of the RPSA family were annotated by comparative mapping and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) localization. Transcription was investigated in the cerebrum, cerebellum, spleen, muscle, lymph node, duodenum and blood, and transcripts were detected for 6 of the 11 pseudogenes in some of these tissues.
Conclusions: In the present work we have characterized the ovine RPSA family. Our results have revealed the existence of 11 ovine RPSA pseudogenes and provide new data on their structure and sequence. Such information will facilitate molecular studies of the functional RPSA gene taking into account the existence of these pseudogenes in the design of experiments. It remains to be investigated if the transcribed members are functional as regulatory non-coding RNA or as functional proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the porcine multicopy ribosomal protein SA/37-kDa laminin receptor gene family.Gene. 2007 Jun 15;395(1-2):135-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.02.022. Epub 2007 Mar 15. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17434268
-
Molecular characterization of the full-length coding sequence of the caprine laminin receptor gene (RPSA).Biochem Genet. 2010 Dec;48(11-12):962-9. doi: 10.1007/s10528-010-9378-4. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Biochem Genet. 2010. PMID: 20839046
-
Variable levels of 37-kDa/67-kDa laminin receptor (RPSA) mRNA in ovine tissues: potential contribution to the regulatory processes of PrPSc propagation?Anim Biotechnol. 2009;20(3):151-5. doi: 10.1080/10495390902996863. Anim Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19544211
-
Looking into laminin receptor: critical discussion regarding the non-integrin 37/67-kDa laminin receptor/RPSA protein.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016 May;91(2):288-310. doi: 10.1111/brv.12170. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016. PMID: 25630983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual role of ribosomal protein SA in pathogen infection: the key role of structure and localization.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Sep 4;51(1):952. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09883-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39230600 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel polysome messages and changes in translational activity appear after induction of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells.BMC Mol Biol. 2012 Mar 21;13:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-13-9. BMC Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22436005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orihuela CJ, Mahdavi J, Thornton J, Mann B, Wooldridge KG, Abouseada N, Oldfield NJ, Self T, Ala'Aldeen DA, Tuomanen EI. Laminin receptor initiates bacterial contact with the blood brain barrier in experimental meningitis models. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1638–1646. doi: 10.1172/JCI36759. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

