The characteristics of impaired fasting glucose associated with obesity and dyslipidaemia in a Chinese population
- PMID: 20233452
- PMCID: PMC2851684
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-139
The characteristics of impaired fasting glucose associated with obesity and dyslipidaemia in a Chinese population
Abstract
Background: Different populations have diverse patterns of relationships between Impaired Fasting Glucose (IFG) and obesity and lipid markers, it is important to investigate the characteristics of associations between IFG and other related risk factors including body mass index (BMI), waist circumstance (WC), serum lipids and blood pressure (BP) in a Chinese population.
Methods: This was a case-control study of 648 IFG subjects and 1,296 controls derived from a large-scale, community-based, cross-sectional survey of 10,867 participants. Each subject received a face-to-face interview, physical examination, and blood tests, including fasting blood glucose and lipids. Student's t-test, Chi-square test, Spearman correlation and multiple logistic regressions were used for the statistical analyses.
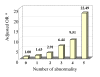
Results: Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) was positively correlated with BMI, WC, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC), and was negatively correlated with high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) (all p < 0.05). BMI was more strongly correlated with IFG than with WC. The correlation coefficient of FPG was remarkably higher with TG (0.244) than with TC (0.134) and HDL-C (-0.192). TG was an important predictor of IFG, with odds ratios of 1.76 (95%CI: 1.31-2.36) for subjects with borderline high TG level (1.70 mmol/l < or = TG < 2.26 mmol/l) and 3.13 (95% CI: 2.50-3.91) for those with higher TG level (TG > or = 2.26 mmol/l), when comparing to subjects with TG < 1.70 mmol/l. There was a significant dose-response relationship between the number of abnormal variables and increased risk of IFG.
Conclusions: In this Chinese population, both BMI and WC were important predictors of IFG. Abnormal TG as a lipid marker was more strongly associated with IFG than were TC and HDL-C. These factors should be taken into consideration simultaneously for prevention of IFG.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlates of serum lipids and lipoproteins in Congolese patients with arterial hypertension.Cardiovasc J S Afr. 2005 Sep-Oct;16(5):249-55. Cardiovasc J S Afr. 2005. PMID: 16307156
-
[Change in the prevalence of obesity phenotypes and cardiometabolic disorders among children aged 6- 17 in Beijing during 2004- 2013].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jan;50(1):34-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.01.007. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26792501 Chinese.
-
A comparative research on obesity hypertension by the comparisons and associations between waist circumference, body mass index with systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and the clinical laboratory data between four special Chinese adult groups.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018;40(1):16-21. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2017.1281940. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29083240
-
Cardiometabolic and obesity risk outcomes of dawn-to-dusk, dry intermittent fasting: Insights from an umbrella review.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025 Jun;67:127-145. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.03.006. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025. PMID: 40081802
-
Effects of fasting intervention regulating anthropometric and metabolic parameters in subjects with overweight or obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Food Funct. 2020 May 1;11(5):3781-3799. doi: 10.1039/d0fo00287a. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32342961
Cited by
-
A Longitudinal Retrospective Observational Study on Obesity Indicators and the Risk of Impaired Fasting Glucose in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women.J Clin Med. 2022 May 16;11(10):2795. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102795. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35628921 Free PMC article.
-
Individual and combined associations of body mass index and waist circumference with components of metabolic syndrome among multiethnic middle-aged and older adults: A cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 22;14:1078331. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1078331. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36909310 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of hypoalphalipoproteinemia on quality of life in Taiwanese women with central obesity.Qual Life Res. 2014 Jun;23(5):1619-27. doi: 10.1007/s11136-013-0601-8. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Qual Life Res. 2014. PMID: 24322908
-
Effects of AMPD1 gene C34T polymorphism on cardiac index, blood pressure and prognosis in patients with cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Jul 3;17(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0608-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 28673246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The characteristics of pre-diabetic patients associated with body composition and cardiovascular disease risk factors in the Iranian population.J Res Med Sci. 2016 Apr 8;21:20. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.179888. eCollection 2016. J Res Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27904566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care for patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(suppl 1):s1–s85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous