Pooling biomarker data from different studies of disease risk, with a focus on endogenous hormones
- PMID: 20233851
- PMCID: PMC2875156
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0061
Pooling biomarker data from different studies of disease risk, with a focus on endogenous hormones
Abstract
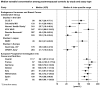
Large numbers of observations are needed to provide adequate power in epidemiologic studies of biomarkers and cancer risk. However, there are currently few large mature studies with adequate numbers of cases with biospecimens available. Therefore, pooling biomarker measures from different studies is a valuable approach, enabling investigators to make robust estimates of risk and to examine associations in subgroups of the population. The ideal situation is to have standardized methods in all studies so that the biomarker data can be pooled in their original units. However, even when the studies do not have standardized methods, as with existing studies on hormones and cancer, a simple approach using study-specific quantiles or percentage increases can provide substantial information on the relationship of the biomarker with cancer risk.
Figures

References
-
- Prospective Studies Collaboration. Lewington S, Whitlock G, Clarke R, et al. Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55,000 vascular deaths. Lancet. 2007;370:1829–39. - PubMed
-
- Santen RJ, Lee JS, Wang S, et al. Potential role of ultra-sensitive estradiol assays in estimating the risk of breast cancer and fractures. Steroids. 2008;73:1318–21. - PubMed
-
- Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group Endogenous sex hormones and breast cancer in postmenopausal women: reanalysis of nine prospective studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:606–16. - PubMed
-
- Kaaks R, Rinaldi S, Key TJ, et al. Postmenopausal serum androgens, oestrogens and breast cancer risk: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:1071–82. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, Ettinger B, Stanczyk FZ, et al. Comparison of methods to measure low serum estradiol levels in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3791–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

