STAT2 contributes to promotion of colorectal and skin carcinogenesis
- PMID: 20233899
- PMCID: PMC2851485
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0105
STAT2 contributes to promotion of colorectal and skin carcinogenesis
Abstract
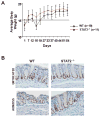
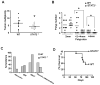
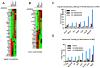
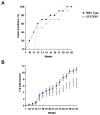
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 (STAT2) is an essential transcription factor in the type I IFN (IFN-alpha/beta) signal transduction pathway and known for its role in mediating antiviral immunity and cell growth inhibition. Unlike other members of the STAT family, IFNs are the only cytokines known to date that can activate STAT2. Given the inflammatory and antiproliferative dual nature of IFNs, we hypothesized that STAT2 prevents inflammation-induced colorectal and skin carcinogenesis by altering the inflammatory immune response. Contrary to our hypothesis, deletion of STAT2 inhibited azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate-induced colorectal carcinogenesis as measured by prolonged survival, lower adenoma incidence, smaller polyps, and less chronic inflammation. STAT2 deficiency also inhibited 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene/12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced skin carcinogenesis as indicated by reduced papilloma multiplicity. A potential mechanism by which STAT2 promotes carcinogenesis is through activation of proinflammatory mediators. Deletion of STAT2 decreased azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate-induced expression and release of proinflammatory mediators, such as interleukin-6 and CCL2, and decreased interleukin-6 release from skin carcinoma cells, which then decreased STAT3 activation. Our findings identify STAT2 as a novel contributor to colorectal and skin carcinogenesis that may act to increase the gene expression and secretion of proinflammatory mediators, which in turn activate the oncogenic STAT3 signaling pathway.
(c) 2010 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Balkwill F, Charles KA, Mantovani A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer cell. 2005;7:211–7. - PubMed
-
- Ekbom A. Risk of cancer in ulcerative colitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 1998;2:312–3. - PubMed
-
- Xiao H, Gulen MF, Qin J, et al. The Toll-interleukin-1 receptor member SIGIRR regulates colonic epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Immunity. 2007;26:461–75. - PubMed
-
- Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, et al. IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 2004;118:285–96. - PubMed
-
- Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, et al. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 2004;431:461–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

