Regulation of aerobic and anaerobic D-malate metabolism of Escherichia coli by the LysR-type regulator DmlR (YeaT)
- PMID: 20233924
- PMCID: PMC2863561
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01665-09
Regulation of aerobic and anaerobic D-malate metabolism of Escherichia coli by the LysR-type regulator DmlR (YeaT)
Abstract
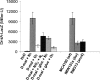
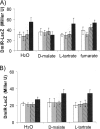
Escherichia coli K-12 is able to grow under aerobic conditions on D-malate using DctA for D-malate uptake and the D-malate dehydrogenase DmlA (formerly YeaU) for converting D-malate to pyruvate. Induction of dmlA encoding DmlA required an intact dmlR (formerly yeaT) gene, which encodes DmlR, a LysR-type transcriptional regulator. Induction of dmlA by DmlR required the presence of D-malate or L- or meso-tartrate, but only D-malate supported aerobic growth. The regulator of general C(4)-dicarboxylate metabolism (DcuS-DcuR two-component system) had some effect on dmlA expression. The anaerobic L-tartrate regulator TtdR or the oxygen sensors ArcB-ArcA and FNR did not have a major effect on dmlA expression. DmlR has a high level of sequence identity (49%) with TtdR, the L- and meso-tartrate-specific regulator of L-tartrate fermentation in E. coli. dmlA was also expressed at high levels under anaerobic conditions, and the bacteria had D-malate dehydrogenase activity. These bacteria, however, were not able to grow on D-malate since the anaerobic pathway for D-malate degradation has a predicted yield of < or = 0 ATP/mol D-malate. Slow anaerobic growth on D-malate was observed when glycerol was also provided as an electron donor, and D-malate was used in fumarate respiration. The expression of dmlR is subject to negative autoregulation. The network for regulation and coordination of the central and peripheral pathways for C(4)-dicarboxylate metabolism by the regulators DcuS-DcuR, DmlR, and TtdR is discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Blumer, C., A. Kleefeld, D. Lehnen, M. Heintz, U. Dobrindt, G. Nagy, K. Michaelis, L. Emödy, T. Polen, R. Rachel, V. F. Wendisch, and G. Unden. 2005. Regulation of type 1 fimbriae synthesis and biofilm formation by the transcriptional regulator LrhA of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 151:3287-3298. - PubMed
-
- Bongaerts, J., S. Zoske, U. Weidner, and G. Unden. 1995. Transcriptional regulation of the proton translocating NADH dehydrogenase genes (nuoA-N) of Escherichia coli by electron acceptors, electron donors and gene regulators. Mol. Microbiol. 16:521-534. - PubMed
-
- Brückner, R., and F. Titgemeyer. 2002. Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: choice of the carbon source and autoregulatory limitation of sugar utilization. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 209:141-148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

