Cyclic-di-GMP-mediated repression of swarming motility by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the pilY1 gene and its impact on surface-associated behaviors
- PMID: 20233936
- PMCID: PMC2901681
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01642-09
Cyclic-di-GMP-mediated repression of swarming motility by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the pilY1 gene and its impact on surface-associated behaviors
Abstract
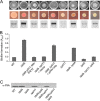
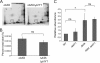
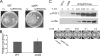
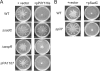
The intracellular signaling molecule cyclic-di-GMP (c-di-GMP) has been shown to influence surface-associated behaviors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including biofilm formation and swarming motility. Previously, we reported a role for the bifA gene in the inverse regulation of biofilm formation and swarming motility. The bifA gene encodes a c-di-GMP-degrading phosphodiesterase (PDE), and the Delta bifA mutant exhibits increased cellular pools of c-di-GMP, forms hyperbiofilms, and is unable to swarm. In this study, we isolated suppressors of the Delta bifA swarming defect. Strains with mutations in the pilY1 gene, but not in the pilin subunit pilA gene, show robust suppression of the swarming defect of the Delta bifA mutant, as well as its hyperbiofilm phenotype. Despite the ability of the pilY1 mutation to suppress all the c-di-GMP-related phenotypes, the global pools of c-di-GMP are not detectably altered in the Delta bifA Delta pilY1 mutant relative to the Delta bifA single mutant. We also show that enhanced expression of the pilY1 gene inhibits swarming motility, and we identify residues in the putative VWA domain of PilY1 that are important for this phenotype. Furthermore, swarming repression by PilY1 specifically requires the diguanylate cyclase (DGC) SadC, and epistasis analysis indicates that PilY1 functions upstream of SadC. Our data indicate that PilY1 participates in multiple surface behaviors of P. aeruginosa, and we propose that PilY1 may act via regulation of SadC DGC activity but independently of altering global c-di-GMP levels.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Minor pilins of the type IV pilus system participate in the negative regulation of swarming motility.J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(19):5388-403. doi: 10.1128/JB.00899-12. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22865844 Free PMC article.
-
BifA, a cyclic-Di-GMP phosphodiesterase, inversely regulates biofilm formation and swarming motility by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14.J Bacteriol. 2007 Nov;189(22):8165-78. doi: 10.1128/JB.00586-07. Epub 2007 Jun 22. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17586641 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cyclic Di-GMP and Exopolysaccharide in Type IV Pilus Dynamics.J Bacteriol. 2017 Mar 28;199(8):e00859-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00859-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28167523 Free PMC article.
-
c-di-GMP and its Effects on Biofilm Formation and Dispersion: a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Review.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MB-0003-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0003-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taming the flagellar motor of pseudomonads with a nucleotide messenger.Environ Microbiol. 2020 Jul;22(7):2496-2513. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15036. Epub 2020 May 5. Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32329141 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordination of swarming motility, biosurfactant synthesis, and biofilm matrix exopolysaccharide production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Nov;80(21):6724-32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01237-14. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25172852 Free PMC article.
-
PilY1 regulates the dynamic architecture of the type IV pilus machine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 30;15(1):9382. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53638-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39477930 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of flagellar motor switching by c-di-GMP phosphodiesterases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Biol Chem. 2019 Sep 13;294(37):13789-13799. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009009. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31350333 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel factors involved in modulating motility of Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 4;9(11):e111513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111513. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25369209 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa minor pilins prime type IVa pilus assembly and promote surface display of the PilY1 adhesin.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 2;290(1):601-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.616904. Epub 2014 Nov 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25389296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldridge, P., R. Paul, P. Goymer, P. Rainey, and U. Jenal. 2003. Role of the GGDEF regulator PleD in polar development of Caulobacter crescentus. Mol. Microbiol. 47:1695-1708. - PubMed
-
- Alm, R. A., J. P. Hallinan, A. A. Watson, and J. S. Mattick. 1996. Fimbrial biogenesis genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pilW and pilX increase the similarity of type 4 fimbriae to the GSP protein-secretion systems and pilY1 encodes a gonococcal PilC homologue. Mol. Microbiol. 22:161-173. - PubMed
-
- Alm, R. A., and J. S. Mattick. 1995. Identification of a gene, pilV, required for type 4 fimbrial biogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, whose product possesses a pre-pilin-like leader sequence. Mol. Microbiol. 16:485-496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

