Structure of a DNA polymerase alpha-primase domain that docks on the SV40 helicase and activates the viral primosome
- PMID: 20234039
- PMCID: PMC2878050
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.116830
Structure of a DNA polymerase alpha-primase domain that docks on the SV40 helicase and activates the viral primosome
Abstract
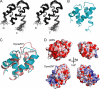
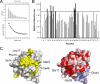
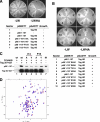
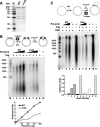
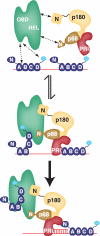
DNA polymerase alpha-primase (pol-prim) plays a central role in DNA replication in higher eukaryotes, initiating synthesis on both leading and lagging strand single-stranded DNA templates. Pol-prim consists of a primase heterodimer that synthesizes RNA primers, a DNA polymerase that extends them, and a fourth subunit, p68 (also termed B-subunit), that is thought to regulate the complex. Although significant knowledge about single-subunit primases of prokaryotes has accumulated, the functions and regulation of pol-prim remain poorly understood. In the SV40 replication model, the p68 subunit is required for primosome activity and binds directly to the hexameric viral helicase T antigen, suggesting a functional link between T antigen-p68 interaction and primosome activity. To explore this link, we first mapped the interacting regions of the two proteins and discovered a previously unrecognized N-terminal globular domain of p68 (p68N) that physically interacts with the T antigen helicase domain. NMR spectroscopy was used to determine the solution structure of p68N and map its interface with the T antigen helicase domain. Structure-guided mutagenesis of p68 residues in the interface diminished T antigen-p68 interaction, confirming the interaction site. SV40 primosome activity of corresponding pol-prim mutants decreased in proportion to the reduction in p68N-T antigen affinity, confirming that p68-T antigen interaction is vital for primosome function. A model is presented for how this interaction regulates SV40 primosome activity, and the implications of our findings are discussed in regard to the molecular mechanisms of eukaryotic DNA replication initiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A specific docking site for DNA polymerase {alpha}-primase on the SV40 helicase is required for viral primosome activity, but helicase activity is dispensable.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):33475-33484. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.156240. Epub 2010 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20685648 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the interaction of a hexameric replicative helicase with the regulatory subunit of human DNA polymerase α-primase.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 3;287(32):26854-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.363655. Epub 2012 Jun 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22700977 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T-antigen primosome activities in viral DNA replication.J Virol. 2002 May;76(10):5121-30. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.10.5121-5130.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11967327 Free PMC article.
-
The Pol α-primase complex.Subcell Biochem. 2012;62:157-69. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4572-8_9. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22918585 Review.
-
The DNA polymerase alpha-primase complex: multiple functions and interactions.ScientificWorldJournal. 2003 Mar 17;3:21-33. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2003.05. ScientificWorldJournal. 2003. PMID: 12806117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How Pol α-primase is targeted to replisomes to prime eukaryotic DNA replication.Mol Cell. 2023 Aug 17;83(16):2911-2924.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.06.035. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37506699 Free PMC article.
-
Replication Protein A, the Main Eukaryotic Single-Stranded DNA Binding Protein, a Focal Point in Cellular DNA Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):588. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010588. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lagging Strand Initiation Processes in DNA Replication of Eukaryotes-Strings of Highly Coordinated Reactions Governed by Multiprotein Complexes.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;14(5):1012. doi: 10.3390/genes14051012. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human DNA helicase B (HDHB) binds to replication protein A and facilitates cellular recovery from replication stress.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6469-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.324582. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22194613 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal domain of the DNA polymerase catalytic subunit regulates the primase and polymerase activities of the human DNA polymerase α-primase complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 8;289(32):22021-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.570333. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24962573 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

