Heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunogenicity in very-low-birth-weight, premature infants
- PMID: 20234331
- PMCID: PMC2949965
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181d264a6
Heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunogenicity in very-low-birth-weight, premature infants
Abstract
Background: The heptavalent pneumococcal CRM197 conjugate vaccine (PCV-7) has been incompletely studied in very-low-birth-weight (< or =1500 g) infants.
Objective: To assess PCV-7 immunogenicity in very-low-birth-weight, premature infants. We hypothesized that the frequency of postvaccine antibody concentrations > or =0.15 microg/mL would vary directly with birth weight.
Methods: This was a multicenter observational study. Infants 401 to 1500 g birth weight and <32 0/7 weeks gestation, stratified by birth weight, were enrolled from 9 National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network centers. Infants received PCV-7 at 2, 4, and 6 months after birth and had blood drawn 4 to 6 weeks following the third dose. Antibodies against the 7 vaccine serotypes were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
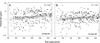
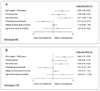
Results: Of 369 enrolled infants, 244 completed their primary vaccine series by 8 months and had serum obtained. Subjects were 27.8 +/- 2.2 (mean +/- standard deviation) weeks gestation and 1008 +/- 282 g birth weight. Twenty-six percent had bronchopulmonary dysplasia and 16% had received postnatal glucocorticoids. Infants 1001 to 1500 g birth weight were more likely than those 401 to 1000 g to achieve antibody concentrations > or =0.15 microg/mL against the least 2 immunogenic serotypes (6B: 96% vs. 85%, P = 0.003 and 23F: 97% vs. 88%, P = 0.009). In multiple logistic regression analysis, lower birth weight, postnatal glucocorticoid use, lower weight at blood draw, and Caucasian race were each independently associated with antibody concentrations <0.35 microg/mL against serotypes 6B and/or 23F.
Conclusions: When compared with larger premature infants, infants weighing < or =1000 g at birth have similar antibody responses to most, but not all, PCV-7 vaccine serotypes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00273325.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors confirm that they made substantial contributions to the work, were involved in the drafting and/or reviewing of the article, and have approved the version to be published. No author has a relevant financial interest or other conflict of interest as regards this research.
Figures

References
-
- Zangwill KM, Vadheim CM, Vannier AM, Hemenway LS, Greenberg DP, Ward JI. Epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease in southern California: implications for the design and conduct of a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine efficacy trial. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1996;174:752–759. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preventing pneumococcal disease among infants and young children: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MMWR. 2000;29(No. RR-9):1–35. - PubMed
-
- Shinefield H, Black S, Ray P, Fireman B, Schwalbe J, Lewis E. Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in low birth weight and preterm infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002;21:182–186. - PubMed
-
- Rennels MB, Edwards KM, Keyserling HL, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of heptavalent pneumococcal vaccine conjugated to CRM197 in United States infants. Pediatrics. 1998;101:604–611. - PubMed
-
- Black S, Shinefield H, Fireman B, et al. Northern California Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center Group. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000;19:187–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI030021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

