Lysophosphatidic acid production and action: critical new players in breast cancer initiation and progression
- PMID: 20234370
- PMCID: PMC2844037
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605588
Lysophosphatidic acid production and action: critical new players in breast cancer initiation and progression
Abstract
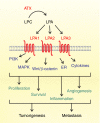
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a potent lipid mediator that acts on a series of specific G protein-coupled receptors, leading to diverse biological actions. Lysophosphatidic acid induces cell proliferation, survival and migration, which are critically required for tumour formation and metastasis. This bioactive lipid is produced by the ectoenzyme lysophospholipase D or autotaxin (ATX), earlier known as an autocrine motility factor. The ATX-LPA signalling axis has emerged as an important player in many types of cancer. Indeed, aberrant expression of ATX and LPA receptors occurs during the development and progression of breast cancer. Importantly, expression of either ATX or LPA receptors in the mammary gland of transgenic mice is sufficient to induce the development of a high frequency of invasive and metastatic mammary cancers. The focus of research now turns to understanding the mechanisms by which ATX and LPA promote mammary tumourigenesis and metastasis. Targeting the ATX-LPA signalling axis for drug development may further improve outcomes in patients with breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidic acids, cyclic phosphatidic acids and autotaxin as promising targets in therapies of cancer and other diseases.Acta Biochim Pol. 2008;55(2):227-40. Epub 2008 Jun 14. Acta Biochim Pol. 2008. PMID: 18560605 Review.
-
Mammary tumorigenesis through LPA receptor signaling.Cancer Cell. 2009 Jun 2;15(6):457-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.05.003. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19477423
-
Autotaxin, a secreted lysophospholipase D, is essential for blood vessel formation during development.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;26(13):5015-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02419-05. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16782887 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid receptors increases mammary tumorigenesis, invasion, and metastases.Cancer Cell. 2009 Jun 2;15(6):539-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.03.027. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19477432 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and biological activities of the autotaxin-LPA axis.Prog Lipid Res. 2007 Mar;46(2):145-60. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2007.02.001. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Prog Lipid Res. 2007. PMID: 17459484 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein Kinase D1 Signaling in Cancer Stem Cells with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity.Cells. 2022 Dec 1;11(23):3885. doi: 10.3390/cells11233885. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497140 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression of the lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 is a target of transforming growth factor beta.Oncogene. 2013 Jun 27;32(26):3198-206. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.325. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22824789 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid-induced p21Waf1 expression mediates the cytostatic response of breast and ovarian cancer cells to TGFβ.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Nov;9(11):1562-70. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0340. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21890597 Free PMC article.
-
Serum ATX as a novel biomarker for breast cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(13):e14973. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014973. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30921203 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles as a promising source of lipid biomarkers for breast cancer detection in blood plasma.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Mar;13(3):e12419. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12419. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38443328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker DL, Fujiwara Y, Pigg KR, Tsukahara R, Kobayashi S, Murofushi H, Uchiyama A, Murakami-Murofushi K, Koh E, Bandle RW, Byun HS, Bittman R, Fan D, Murph M, Mills GB, Tigyi G (2006) Carba analogs of cyclic phosphatidic acid are selective inhibitors of autotaxin and cancer cell invasion and metastasis. J Biol Chem 281: 22786–22793 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black EJ, Clair T, Delrow J, Neiman P, Gillespie DA (2004) Microarray analysis identifies autotaxin, a tumour cell motility and angiogenic factor with lysophospholipase D activity, as a specific target of cell transformation by v-Jun. Oncogene 23: 2357–2366 - PubMed
-
- Caldas-Lopes E, Cerchietti L, Ahn JH, Clement CC, Robles AI, Rodina A, Moulick K, Taldone T, Gozman A, Guo Y, Wu N, de Stanchina E, White J, Gross SS, Ma Y, Varticovski L, Melnick A, Chiosis G (2009) Hsp90 inhibitor PU-H71, a multimodal inhibitor of malignancy, induces complete responses in triple-negative breast cancer models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 8368–8373 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

