A robust gene selection method for microarray-based cancer classification
- PMID: 20234770
- PMCID: PMC2834377
- DOI: 10.4137/cin.s3794
A robust gene selection method for microarray-based cancer classification
Abstract
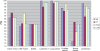
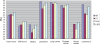
Gene selection is of vital importance in molecular classification of cancer using high-dimensional gene expression data. Because of the distinct characteristics inherent to specific cancerous gene expression profiles, developing flexible and robust feature selection methods is extremely crucial. We investigated the properties of one feature selection approach proposed in our previous work, which was the generalization of the feature selection method based on the depended degree of attribute in rough sets. We compared the feature selection method with the established methods: the depended degree, chi-square, information gain, Relief-F and symmetric uncertainty, and analyzed its properties through a series of classification experiments. The results revealed that our method was superior to the canonical depended degree of attribute based method in robustness and applicability. Moreover, the method was comparable to the other four commonly used methods. More importantly, the method can exhibit the inherent classification difficulty with respect to different gene expression datasets, indicating the inherent biology of specific cancers.
Keywords: cancer classification; dependent degree; feature selection; machine learning; microarrays; rough sets.
Figures
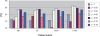
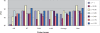




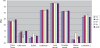
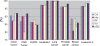
References
-
- Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, et al. Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science. 1999;286(5439):531–7. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Wong L. Identifying good diagnostic gene groups from gene expression profiles using the concept of emerging patterns. Bioinformatics. 2002;18(5):725–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

