Valsartan addition to amlodipine is more effective than losartan addition in hypertensive patients inadequately controlled by amlodipine
- PMID: 20234783
- PMCID: PMC2835558
- DOI: 10.2147/vhrm.s9404
Valsartan addition to amlodipine is more effective than losartan addition in hypertensive patients inadequately controlled by amlodipine
Abstract
Introduction: This study evaluated the effects on blood pressure (BP) of valsartan 160 mg or losartan 100 mg addition to amlodipine 5 mg in hypertensive patients.
Methods: 221 patients with inadequately controlled BP (DBP >or= 90 mmHg) after 4 weeks of treatment with amlodipine 5 mg were randomized to receive losartan/amlodipine combination therapy or valsartan/amlodipine combination therapy for 4 weeks in a cross-over study design. At the end of the wash-out period and of each treatment period, clinic and ambulatory BP measurements were recorded.
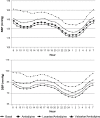
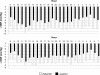
Results: 166 patients completed the study. Both combination treatments induced a greater ambulatory BP reduction than did monotherapy. However, the further mean reductions in BP versus monotherapy were significantly greater with the valsartan/amlodipine combination (SBP/DBP: -7.9 +/- 3.4/-6.5 +/- 2.6 mmHg for 24-hour, -8.0 +/- 3.4/-6.6 +/- 2.7 mmHg for daytime; -7.7 +/- 3.3/-6.4 +/- 2.7 mmHg for nighttime) than with the losartan/amlodipine combination (SBP/DBP: -5.5 +/- 2.8/-4.2 +/- 2.1 mmHg for 24-hour, -5.7 +/- 2.9/-4.4 +/- 2.2 mmHg for daytime; -4.8 +/- 2.8/-3.7 +/- 2.2 mmHg for nighttime; P < 0.01 vs valsartan/amlodipine). The incidence of adverse events with valsartan/amlodipine (8%) and losartan/amlodipine (9%) was lower than that observed with amlodipine monotherapy (17%; P < 0.05 vs combinations).
Conclusion: Valsartan 160 mg plus amlodipine 5 mg produced greater BP reductions than losartan 100 mg plus amlodipine 5 mg.
Keywords: ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; amlodipine; angiotensin receptor blocker; combination therapy; losartan; valsartan.
Figures

Similar articles
-
24-hour ambulatory blood-pressure effects of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide combinations compared with amlodipine in hypertensive patients at increased cardiovascular risk: a VAST sub-study.Blood Press Monit. 2005 Apr;10(2):85-91. doi: 10.1097/00126097-200504000-00006. Blood Press Monit. 2005. PMID: 15812256 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of amlodipine/valsartan combination therapy in hypertensive patients not adequately controlled on amlodipine monotherapy.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Nov;25(11):2655-62. doi: 10.1185/03007990903251193. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19751115 Clinical Trial.
-
Tolerability and blood pressure-lowering efficacy of the combination of amlodipine plus valsartan compared with lisinopril plus hydrochlorothiazide in adult patients with stage 2 hypertension.Clin Ther. 2007 Feb;29(2):279-89. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.02.003. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 17472820 Clinical Trial.
-
Amlodipine/valsartan single-pill combination: a review of its use in the management of hypertension.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009;9(5):309-30. doi: 10.2165/11201120-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19791840 Review.
-
Indirect treatment comparison between fixed-dose-combinations of amlodipine/losartan and amlodipine/valsartan in blood pressure control.Int J Clin Pract. 2014 Feb;68(2):163-72. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12343. Int J Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 24460615 Review.
Cited by
-
Renoprotective effects of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni), amlodipine, valsartan, and losartan in gentamycin-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat model: Biochemical, hematological and histological approaches.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Jul 11;6:683-691. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.07.003. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31372346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 Report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- European Society of Hypertension-European Society of Cardiology Guidelines Committee 2003 European Society of Hypertension/European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens. 2003;21:1011–1053. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull E. Effects of different blood-pressure lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively-designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet. 2003;362:1527–1535. - PubMed
-
- Staessen JA, Wang JG, Thijs L. Cardiovascular prevention and blood pressure reduction: a quantitative overview updated until March 1, 2003. J Hypertens. 2003;21:1055–1076. - PubMed
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, et al. for the HOT study group Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the hypertension optimal treatment (HOT) randomised trial. Lancet. 1998;351:1755–1762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

