Modulation of cell surface expression of nonactivated cholecystokinin receptors using bivalent ligand-induced internalization
- PMID: 20235611
- PMCID: PMC3593351
- DOI: 10.1021/jm100135g
Modulation of cell surface expression of nonactivated cholecystokinin receptors using bivalent ligand-induced internalization
Abstract
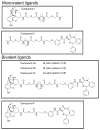
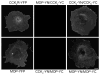
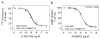
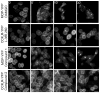
CCK(2) receptor antagonists potentiate pain relief by MOP receptor agonists. In an attempt to enhance this effect, we prepared bivalent ligands incorporating CCK(2) receptor antagonist and MOP receptor agonist pharmacophores. (9) Ligands with 16- to 22-atom spacers could simultaneously bind both receptors but provided no advantage in activity over individual ligands. We now examine the effect of these ligands on receptor internalization as a mechanism of receptor regulation. We prepared CHO cell lines expressing nonfluorescent halves (YN and YC) of yellow fluorescent protein attached to each receptor. Spatial approximation of constructs was needed to yield fluorescence. Monovalent MOP agonist 1 signaled normally and internalized the MOP receptor. Monovalent CCK(2) antagonist 2 did not stimulate receptor internalization. In the dual receptor-bearing cells, bivalent ligands 3a-c capable of simultaneously binding both receptors resulted in cell surface fluorescence and internalization of the fluorescent complex in a time- and temperature-dependent manner. Bivalent ligand 4 with spacer too short to occupy both receptors simultaneously yielded no signal. Receptor tethering with appropriate bivalent ligands can down-regulate signaling by moving a nonactivated receptor into the endocytic pathway.
Figures
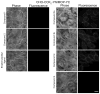
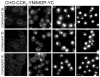
References
-
- Daniels DJ, Kulkarni A, Xie Z, Bhushan RG, Portoghese PS. A bivalent ligand (KDAN-18) containing delta-antagonist and kappa-agonist pharmacophores bridges delta2 and kappa1 opioid receptor phenotypes. J Med Chem. 2005;48:1713–1716. - PubMed
-
- Erez M, Takemori AE, Portoghese PS. Narcotic antagonistic potency of bivalent ligands which contain beta-naltrexamine. Evidence for bridging between proximal recognition sites. J Med Chem. 1982;25:847–849. - PubMed
-
- Faris PL, Komisaruk BR, Watkins LR, Mayer DJ. Evidence for the neuropeptide cholecystokinin as an antagonist of opiate analgesia. Science. 1983;219:310–312. - PubMed
-
- Lu L, Huang M, Liu Z, Ma L. Cholecystokinin-B receptor antagonists attenuate morphine dependence and withdrawal in rats. NeuroReport. 2000;11:829–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

