The virologic and immunologic effects of cyclosporine as an adjunct to antiretroviral therapy in patients treated during acute and early HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 20235838
- PMCID: PMC2851487
- DOI: 10.1086/651664
The virologic and immunologic effects of cyclosporine as an adjunct to antiretroviral therapy in patients treated during acute and early HIV-1 infection
Abstract
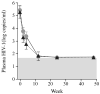
Acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection is characterized by high levels of immune activation. Immunomodulation with cyclosporine combined with antiretroviral therapy (ART) in the setting of acute and early HIV-1 infection has been reported to result in enhanced immune reconstitution. Fifty-four individuals with acute and early infection were randomized to receive ART with 4 weeks of cyclosporine versus ART alone. In 48 subjects who completed the study, there were no significant differences between treatment arms in levels of proviral DNA or CD4(+) T cell counts. Adjunctive therapy with cyclosporine in this setting does not provide apparent virologic or immunologic benefit.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Schacker TW, Hughes JP, Shea T, Coombs RW, Corey L. Biological and virologic characteristics of primary HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128:613–20. - PubMed
-
- Hoen B, Cooper DA, Lampe FC, et al. Predictors of virological outcome and safety in primary HIV type 1-infected patients initiating quadruple antiretroviral therapy: QUEST GW PROB3005. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:381–90. - PubMed
-
- Markowitz M, Vesanen M, Tenner-Racz K, et al. The effect of commencing combination antiretroviral therapy soon after human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on viral replication and antiviral immune responses. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:527–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI41530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-69501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 27665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI041534/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 27661/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI041534/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027661/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI41531/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI041530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046370/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI43638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI041531/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 46370/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

