Stimulation of lateral hypothalamic glutamate and acetylcholine efflux by nicotine: implications for mechanisms of nicotine-induced activation of orexin neurons
- PMID: 20236223
- PMCID: PMC2860645
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06666.x
Stimulation of lateral hypothalamic glutamate and acetylcholine efflux by nicotine: implications for mechanisms of nicotine-induced activation of orexin neurons
Abstract
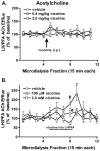
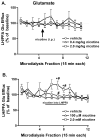
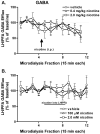
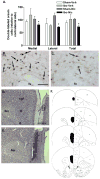
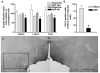
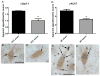
The hypothalamus is a prominent target of nicotine action. We have previously shown that acute systemic nicotine treatment induces Fos expression in the lateral hypothalamus and perifornical area (LH/PFA), with orexin/hypocretin neurons being particularly responsive. However, the neurochemical correlates of acute nicotine treatment in the LH/PFA have not been described. Anatomical studies have revealed that this area receives afferents from cholinergic, glutamatergic, and GABAergic telencephalic brain regions, suggesting a potential role for these neurotransmitters in mediating the hypothalamic component of nicotine effects on homeostatic phenomena, such as arousal and appetite. Here, we used in vivo microdialysis to determine the effect of acute systemic or local nicotine on glutamate, acetylcholine, and GABA efflux in the LH/PFA of rats. Local administration of nicotine significantly increased acetylcholine and glutamate, but not GABA, in the LH/PFA. Thus, we further tested the role of afferent sources of glutamate and acetylcholine in mediating acute nicotine-induced activation of orexin neurons by unilaterally lesioning the prefrontal cortex or basal forebrain cholinergic regions. Lesioned animals showed reduced Fos-positive orexin neurons following nicotine treatment. These data suggest that both acetylcholine and glutamate may mediate the effects of acute nicotine on the activity of hypothalamic neurons, including orexin/hypocretin cells. Changes in cholinergic or glutamatergic transmission in this region with chronic nicotine may contribute to long-term alterations in functions mediated by LH/PFA neurons, including feeding and arousal.
Figures
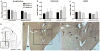
Similar articles
-
Stimulation of cortical acetylcholine release by orexin A.Neuroscience. 2005;130(2):541-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.09.050. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15664710
-
Orexin B/hypocretin 2 increases glutamatergic transmission to ventral tegmental area neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Oct;28(8):1545-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06397.x. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18793323
-
Dopaminergic regulation of orexin neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jun;21(11):2993-3001. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04121.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15978010
-
Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):R572-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00674.2010. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21697524 Review.
-
Lateral hypothalamic orexin/hypocretin neurons: A role in reward-seeking and addiction.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:74-90. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.106. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19815001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of cholinergic mechanisms in the behavioral effects of dietary fat consumption.Brain Res. 2012 Aug 27;1470:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22765913 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signaling in the Hypothalamus: Mechanisms Related to Nicotine's Effects on Food Intake.Nicotine Tob Res. 2020 Feb 6;22(2):152-163. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntz010. Nicotine Tob Res. 2020. PMID: 30690485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic regulation of energy homeostasis.Nicotine Tob Res. 2012 Nov;14(11):1270-90. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nts159. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Nicotine Tob Res. 2012. PMID: 22990212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual orexin receptor antagonist TCS1102 does not affect reinstatement of nicotine-seeking.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 15;12(3):e0173967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173967. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28296947 Free PMC article.
-
The novel α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist EVP-6124 enhances dopamine, acetylcholine, and glutamate efflux in rat cortex and nucleus accumbens.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Dec;231(23):4541-51. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3596-0. Epub 2014 May 9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24810107
References
-
- Arnold HM, Nelson CL, Sarter M, Bruno JP. Sensitization of cortical acetylcholine release by repeated administration of nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003;165:346–358. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitogiannis A, Tzschentke TM, Riscaldino L, Wise RA, Shizgal P. Fos expression following self-stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex. Behav Brain Res. 2000;107:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Bubser M, Fadel JR, Jackson LL, Meador-Woodruff JH, Jing D, Deutch AY. Dopaminergic regulation of orexin neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:2993–3001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

