Towards a better understanding of the role of psychological variables in arthritis outcome research
- PMID: 20236498
- PMCID: PMC2875649
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2922
Towards a better understanding of the role of psychological variables in arthritis outcome research
Abstract
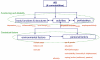
In the previous issue of Arthritis Research and Therapy, Brionez and colleagues show that helplessness, depression, and passive coping account for significant variability in self-reported functional limitations in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, beyond the effect of age, inflammation and radiographic damage. Since the perspective of the patients in the experience of health is increasingly important, insight into the type of psychological variables, the pathways by which they influence health and the approaches for how to deal with these variables are challenging.
Figures
Comment on
-
Psychological correlates of self-reported functional limitation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(6):R182. doi: 10.1186/ar2874. Epub 2009 Dec 7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19968879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2001.
-
- Zautra AJ, Yocum DC, Villanueva I, Smith B, Davis MC, Attrep J, Irwin M. Immune activation and depression in women with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Penninx BW, Kritchevsky SB, Yaffe K, Newman AB, Simonsick EM, Rubin S, Ferruci L, Harris T, Pahor M. Inflammatory markers and depressed mood in older persons: results from the Health, Aging and Body Composition study. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:566–572. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01811-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leventhal HDR, Nerenz DR, Steele D. Illness Representations and Coping with Health Threats. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1984.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

