RHOA and PRKCZ control different aspects of cell motility in pancreatic cancer metastatic clones
- PMID: 20236512
- PMCID: PMC2846889
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-61
RHOA and PRKCZ control different aspects of cell motility in pancreatic cancer metastatic clones
Abstract
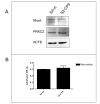
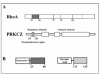
Background: Our understanding of the mechanism regulating pancreatic cancer metastatic phenotype is limited. We analyzed the role of RHOA and PRKCZ in the motility attitude of two subclones of the pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line SUIT-2 (S2), with different in vivo metastatic potential in nude mice: S2-m with a low metastatic potential and highly metastatic S2-CP9 using RHOA and PRKCZ cell-permeable inhibitory peptides.
Methods: Adhesion assays, cell permeable peptides, RHOA activity assay, western blotting
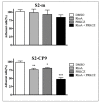
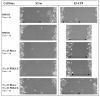
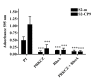
Results: When used in combination cell-permeable inhibitory peptides partially inhibited cell adhesion by about 50% in clone S2-CP9. In clone S2-m, the effect was limited to 15% inhibition. In a wound healing assay, S2-CP9 was sensitive only to treatment with the combination of both RHOA and PRKCZ inhibitory peptides. Conversely, S2-m was unable to migrate toward both ends of the wound in basal conditions. Migration of cells through a membrane with 8 mum pores was completely abolished in both clones by individual treatment with RHOA and PRKCZ inhibitory peptides.
Conclusion: Herein, we demonstrate a critical role for RHOA and PRKCZ in the regulation of different aspects of cell motility of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and demonstrate the need to inhibit both pathways to obtain a functionally relevant effect in most assays. These results indicate that RHOA and PRKCZ, and their downstream effectors, can represent important pharmacological targets that could potentially control the highly metastatic attitude of PDAC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of RhoA in the regulation of cell morphology and motility.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005 May;61(1):21-33. doi: 10.1002/cm.20062. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005. PMID: 15776463
-
Specific induction of migration and invasion of pancreatic carcinoma cells by RhoC, which differs from RhoA in its localisation and activity.Biol Chem. 2009 Oct;390(10):1063-77. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.110. Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19642867
-
RNA interference suppression of MUC1 reduces the growth rate and metastatic phenotype of human pancreatic cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 May 15;12(10):2976-87. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1197. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16707592
-
Wisteria floribunda gall extract inhibits cell migration in mouse B16F1 melanoma cells by regulating CD44 expression and GTP-RhoA activity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Oct 31;102(1):10-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.04.036. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16023319
-
AKAPs competing peptide HT31 disrupts the inhibitory effect of PKA on RhoA activity.Oncol Rep. 2006 Oct;16(4):755-61. Oncol Rep. 2006. PMID: 16969490
Cited by
-
Analysis of transcription profile to reveal altered signaling pathways following the overexpression of human desumoylating isopeptidase 2 in pancreatic cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Dec;12(6):4677-4684. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5298. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28105175 Free PMC article.
-
Cell polarity proteins promote macropinocytosis in response to metabolic stress.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 3;15(1):10541. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54788-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39627191 Free PMC article.
-
Rlip Depletion Alters Oncogene Transcription at Multiple Distinct Regulatory Levels.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 21;14(3):527. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030527. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158795 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral immune cell gene expression changes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first line combination chemotherapy.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057053. Epub 2013 Feb 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451142 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical protein kinase C zeta: potential player in cell survival and cell migration of ovarian cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 14;10(4):e0123528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123528. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25874946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Pancreatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:455–465. - PubMed
-
- Laudanna C, Sorio C, Tecchio C, Butcher EC, Bonora A, Bassi C, Scarpa A. Motility analysis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells reveals a role for the atypical zeta isoform of protein kinase C in cancer cell movement. Lab Invest. 2003;83:1155–1163. doi: 10.1097/01.LAB.0000081390.92179.F3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kitamura N, Iwamura T, Taniguchi S, Yamanari H, Kawano MA, Hollingsworth K, Setoguchi T. High collagenolytic activity in spontaneously highly metastatic variants derived from a human pancreatic cancer cell line (SUIT-2) in nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2000;18:561–571. doi: 10.1023/A:1011900818419. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

