Phencyclidine withdrawal disrupts episodic-like memory in rats: reversal by donepezil but not clozapine
- PMID: 20236574
- PMCID: PMC6485542
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145710000234
Phencyclidine withdrawal disrupts episodic-like memory in rats: reversal by donepezil but not clozapine
Abstract
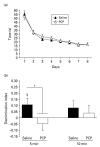
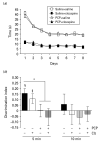
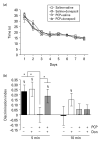
Episodic memory is the capacity to recall an event in time and place (What? Where? When?). Impaired episodic memory is a debilitating cognitive symptom in schizophrenia but is poorly controlled by currently available antipsychotic drugs. Consistent with glutamatergic abnormality in schizophrenia, the NDMA receptor antagonist, phencyclidine (PCP), induces persistent 'schizophrenia-like' symptoms including memory deficits in humans and rodents and is widely used as an animal model of the disorder. However, in contrast to humans, PCP and PCP withdrawal-induced memory deficits in rodents are reversed by antipsychotic drugs such as clozapine. One possible explanation is that the memory tasks used in animal studies do not simultaneously test the What? Where? When? components that characterize episodic memory in human tasks. We investigated whether subchronic PCP withdrawal disrupts memory in rats in a task that requires simultaneous integration of memory for object, place and context. Rats learn to discriminate objects under specific spatial and contextual conditions analogous to the What? Where? When? components of human episodic memory. We found that PCP withdrawal impaired performance on this task and that the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine did not reverse this impairment. However the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) donepezil, which has been shown to improve episodic memory in humans did reverse the effect of PCP. This suggests that PCP withdrawal disruption of object-place-context recognition in rats may prove to be a useful model to investigate episodic memory impairment in schizophrenia and supports the suggestion that AChEIs could prove to be a useful pharmacological strategy to specifically treat episodic memory problems in schizophrenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atypical but not typical antipsychotic drugs ameliorate phencyclidine-induced emotional memory impairments in mice.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019 May;29(5):616-628. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30910381
-
Two novel 5-HT6 receptor antagonists ameliorate scopolamine-induced memory deficits in the object recognition and object location tasks in Wistar rats.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011 Sep;96(2):392-402. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2011.06.015. Epub 2011 Jul 3. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21757018
-
Investigation of the effects of lamotrigine and clozapine in improving reversal-learning impairments induced by acute phencyclidine and D-amphetamine in the rat.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 May;179(2):336-48. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-2058-5. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15645224
-
Postnatal Phencyclidine (PCP) as a Neurodevelopmental Animal Model of Schizophrenia Pathophysiology and Symptomatology: A Review.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016;29:403-428. doi: 10.1007/7854_2015_403. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26510740 Review.
-
Animal models and treatments for addiction and depression co-morbidity.Neurotox Res. 2007 Jan;11(1):1-32. doi: 10.1007/BF03033479. Neurotox Res. 2007. PMID: 17449445 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparing the effects of subchronic phencyclidine and medial prefrontal cortex dysfunction on cognitive tests relevant to schizophrenia.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Nov;232(21-22):3883-97. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4018-7. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26194915
-
Translational Aspects of the Novel Object Recognition Task in Rats Abstinent Following Sub-Chronic Treatment with Phencyclidine (PCP): Effects of Modafinil and Relevance to Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2010 Nov 11;1:146. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2010.00146. eCollection 2010. Front Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 21423454 Free PMC article.
-
Extended-access, but not limited-access, methamphetamine self-administration induces behavioral and nucleus accumbens dopamine response changes in rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Nov;38(10):3487-95. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12361. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24112125 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term associative memory in rats: Effects of familiarization period in object-place-context recognition test.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 30;16(7):e0254570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254570. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34329332 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of schizophrenia.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;164(4):1162-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01386.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21449915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdul-Monim Z, Neill JC, Reynolds GP. Sub-chronic psychotomimetic phencyclidine induces deficits in reversal learning and alterations in parvalbumin-immunoreactive expression in the rat. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2007;21:198–205. - PubMed
-
- Al-Uzri MM, Reveley MA, Owen L, Bruce J, et al. Measuring memory impairment in community-based patients with schizophrenia. Case-control study. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2006;189:132–136. - PubMed
-
- Béracochéa D, Philippin J, Meunier S, Morain P, et al. Improvement of episodic contextual memory by S 18986 in middle-aged mice: comparison with donepezil. Psychopharmacology. 2007;193:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Beraki S, Diaz-Heijtz R, Tai F, Ogren SO. Effects of repeated treatment of phencyclidine on cognition and gene expression in C57BL/6 mice. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;12:243–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

