Unraveling the mechanism of elastic fiber assembly: The roles of short fibulins
- PMID: 20236620
- PMCID: PMC2880191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.03.009
Unraveling the mechanism of elastic fiber assembly: The roles of short fibulins
Abstract
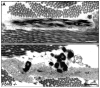
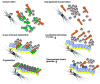
Evolution of elastic fibers is associated with establishment of the closed circulation system. Primary roles of elastic fibers are to provide elasticity and recoiling to tissues and organs and to maintain the structural integrity against mechanical strain over a lifetime. Elastic fibers are comprised of an insoluble elastin core and surrounding mantle of microfibrils. Elastic fibers are formed in a regulated, stepwise manner, which includes the formation of a microfibrillar scaffold, deposition and integration of tropoelastin monomers into the scaffold, and cross-linking of the monomers to form an insoluble, functional polymer. In recent years, an increasing number of glycoproteins have been identified and shown to be located on or surrounding elastic fibers. Among them, the short fibulins-3, -4 and -5 particularly drew attention because of their potent elastogenic activity. Fibulins-3, -4 and -5 are characterized by tandem repeats of calcium binding EGF-like motifs and a C-terminal fibulin module, which is conserved throughout fibulin family members. Initial biochemical characterization and gene expression studies predicted that fibulins might be involved in structural support and/or matrix-cell interactions. Recent analyses of short fibulin knockout mice have revealed their critical roles in elastic fiber development in vivo. We review recent findings on the elastogenic functions of short fibulins and discuss the molecular mechanism underlying their activity in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New insights into elastic fiber assembly.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2007 Dec;81(4):229-40. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20111. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2007. PMID: 18228265 Review.
-
Analysis of dermal elastic fibers in the absence of fibulin-5 reveals potential roles for fibulin-5 in elastic fiber assembly.Matrix Biol. 2009 May;28(4):211-20. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2009.03.004. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Matrix Biol. 2009. PMID: 19321153 Free PMC article.
-
Recent updates on the molecular network of elastic fiber formation.Essays Biochem. 2019 Sep 13;63(3):365-376. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180052. Print 2019 Sep 13. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31395654 Review.
-
Molecular evolution of the fibulins: implications on the functionality of the elastic fibulins.Gene. 2010 Sep 15;464(1-2):17-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Gene. 2010. PMID: 20595023
-
Basic Components of Connective Tissues and Extracellular Matrix: Fibronectin, Fibrinogen, Laminin, Elastin, Fibrillins, Fibulins, Matrilins, Tenascins and Thrombospondins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1348:105-126. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-80614-9_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34807416
Cited by
-
Advances in biomimetic regeneration of elastic matrix structures.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012 Oct;2(5):323-50. doi: 10.1007/s13346-012-0070-6. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 23355960 Free PMC article.
-
Fibulin-4 E57K Knock-in Mice Recapitulate Cutaneous, Vascular and Skeletal Defects of Recessive Cutis Laxa 1B with both Elastic Fiber and Collagen Fibril Abnormalities.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 28;290(35):21443-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.640425. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26178373 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling autosomal recessive cutis laxa type 1C in mice reveals distinct functions for Ltbp-4 isoforms.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Apr;8(4):403-15. doi: 10.1242/dmm.018960. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 25713297 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix molecules facilitating vascular biointegration.J Funct Biomater. 2012 Aug 14;3(3):569-87. doi: 10.3390/jfb3030569. J Funct Biomater. 2012. PMID: 24955633 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-Derived Inflammation Disrupts Elastin Assembly and Alters Saccular Stage Lung Development.Am J Pathol. 2016 Jul;186(7):1786-1800. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.02.016. Epub 2016 May 12. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27181406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Argraves WS, Dickerson K, Burgess WH, Ruoslahti E. Fibulin, a novel protein that interacts with the fibronectin receptor beta subunit cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1989;58:623–9. - PubMed
-
- Broekelmann TJ, Kozel BA, Ishibashi H, Werneck CC, Keeley FW, Zhang L, et al. Tropoelastin interacts with cell-surface glycosaminoglycans via its COOH-terminal domain. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:40939–47. - PubMed
-
- Bunton TE, Biery NJ, Myers L, Gayraud B, Ramirez F, Dietz HC. Phenotypic alteration of vascular smooth muscle cells precedes elastolysis in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome. Circ Res. 2001;88:37–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

