Selectively targeting pain in the trigeminal system
- PMID: 20236764
- PMCID: PMC4704110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.02.016
Selectively targeting pain in the trigeminal system
Abstract
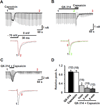
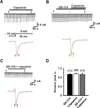
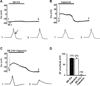
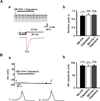
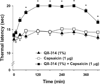
We tested whether it is possible to selectively block pain signals in the orofacial area by delivering the permanently charged lidocaine derivative QX-314 into nociceptors via TPRV1 channels. We examined the effects of co-applied QX-314 and capsaicin on nociceptive, proprioceptive, and motor function in the rat trigeminal system. QX-314 alone failed to block voltage-gated sodium channel currents (I(Na)) and action potentials (APs) in trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons. However, co-application of QX-314 and capsaicin blocked I(Na) and APs in TRPV1-positive TG and dental nociceptive neurons, but not in TRPV1-negative TG neurons or in small neurons from TRPV1 knock-out mice. Immunohistochemistry revealed that TRPV1 is not expressed by trigeminal motor and trigeminal mesencephalic neurons. Capsaicin had no effect on rat trigeminal motor and proprioceptive mesencephalic neurons and therefore should not allow QX-314 to enter these cells. Co-application of QX-314 and capsaicin inhibited the jaw-opening reflex evoked by noxious electrical stimulation of the tooth pulp when applied to a sensory but not a motor nerve, and produced long-lasting analgesia in the orofacial area. These data show that selective block of pain signals can be achieved by co-application of QX-314 with TRPV1 agonists. This approach has potential utility in the trigeminal system for treating dental and facial pain.
Copyright 2010 International Association for the Study of Pain. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
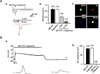
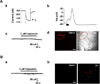
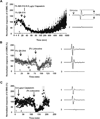
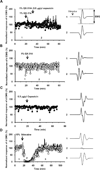
Comment in
-
Capsicum and local anesthetic cocktails for trigeminal pain.Pain. 2010 Jul;150(1):3. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.03.008. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Pain. 2010. PMID: 20356676 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bernardini N, Neuhuber W, Reeh PW, Sauer SK. Morphological evidence for functional capsaicin receptor expression and calcitonin gene-related peptide exocytosis in isolated peripheral nerve axons of the mouse. Neuroscience. 2004;126:585–590. - PubMed
-
- Binshtok AM, Bean BP, Woolf CJ. Inhibition of nociceptors by TRPV1-mediated entry of impermeant sodium channel blockers. Nature. 2007;449:607–610. - PubMed
-
- Binshtok AM, Gerner P, Oh SB, Puopolo M, Suzuki S, Roberson DP, Herbert T, Wang CF, Kim D, Chung G, Mitani AA, Wang GK, Bean BP, Woolf CJ. Coapplication of lidocaine and the permanently charged sodium channel blocker QX-314 produces a long-lasting nociceptive blockade in rodents. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:127–137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Butterworth J, Oxford GS. Local anesthetics: a new hydrophilic pathway for the drug-receptor reaction. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:12–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

