Thyroid hormone regulates hepatic expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 in a PPARalpha-dependent manner
- PMID: 20236931
- PMCID: PMC2863226
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C110.107375
Thyroid hormone regulates hepatic expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 in a PPARalpha-dependent manner
Abstract
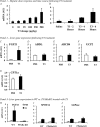
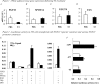
Thyroid hormone has profound and diverse effects on liver metabolism. Here we show that tri-iodothyronine (T3) treatment in mice acutely and specifically induces hepatic expression of the metabolic regulator fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). Mice treated with T3 showed a dose-dependent increase in hepatic FGF21 expression with significant induction at doses as low as 100 microg/kg. Time course studies determined that induction is seen as early as 4 h after treatment with a further increase in expression at 6 h after injection. As FGF21 expression is downstream of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha), we treated PPARalpha knock-out mice with T3 and found no increase in expression, indicating that hepatic regulation of FGF21 by T3 in liver is via a PPARalpha-dependent mechanism. In contrast, in white adipose tissue, FGF21 expression was suppressed by T3 treatment, with other T3 targets unaffected. In cell culture studies with an FGF21 reporter construct, we determined that three transcription factors are required for induction of FGF21 expression: thyroid hormone receptor beta (TRbeta), retinoid X receptor (RXR), and PPARalpha. These findings indicate a novel regulatory pathway whereby T3 positively regulates hepatic FGF21 expression, presenting a novel therapeutic target for diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone receptor regulates most genes independently of fibroblast growth factor 21 in liver.J Endocrinol. 2015 Mar;224(3):289-301. doi: 10.1530/JOE-14-0440. Epub 2014 Dec 11. J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25501997
-
Upregulation of rat liver PPARα-FGF21 signaling by a docosahexaenoic acid and thyroid hormone combined protocol.Biofactors. 2016 Nov 12;42(6):638-646. doi: 10.1002/biof.1300. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Biofactors. 2016. PMID: 27248050
-
Liver-enriched transcription factor CREBH interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α to regulate metabolic hormone FGF21.Endocrinology. 2014 Mar;155(3):769-82. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1490. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24424044 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid sensing by PPARα: Role in controlling hepatocyte gene regulatory networks and the metabolic response to fasting.Prog Lipid Res. 2024 Nov;96:101303. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2024.101303. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Prog Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 39521352 Review.
-
The Nuanced Metabolic Functions of Endogenous FGF21 Depend on the Nature of the Stimulus, Tissue Source, and Experimental Model.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 3;12:802541. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.802541. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35046901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Exercise in the Interplay between Myokines, Hepatokines, Osteokines, Adipokines, and Modulation of Inflammation for Energy Substrate Redistribution and Fat Mass Loss: A Review.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 26;12(6):1899. doi: 10.3390/nu12061899. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32604889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Responsiveness to thyroid hormone and to ambient temperature underlies differences between brown adipose tissue and skeletal muscle thermogenesis in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity.Endocrinology. 2011 Sep;152(9):3571-81. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1066. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21771890 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between the thyroid and liver: a new target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatment.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 7;19(45):8238-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8238. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24363514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights into the pathological development of dyslipidemia in patients with hypothyroidism.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Jun 1;22(3):326-339. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.6606. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34784265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth hormone induces hepatic production of fibroblast growth factor 21 through a mechanism dependent on lipolysis in adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 7;286(40):34559-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.285965. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21849508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hulbert A. J. (2000) Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 75, 519–631 - PubMed
-
- Klieverik L. P., Coomans C. P., Endert E., Sauerwein H. P., Havekes L. M., Voshol P. J., Rensen P. C., Romijn J. A., Kalsbeek A., Fliers E. (2009) Endocrinology 150, 5639–5648 - PubMed
-
- Perra A., Simbula G., Simbula M., Pibiri M., Kowalik M. A., Sulas P., Cocco M. T., Ledda-Columbano G. M., Columbano A. (2008) FASEB J. 22, 2981–2989 - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A., Shanafelt A. B. (2009) Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 10, 359–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

