USF and NF-E2 cooperate to regulate the recruitment and activity of RNA polymerase II in the beta-globin gene locus
- PMID: 20236933
- PMCID: PMC2871457
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.098376
USF and NF-E2 cooperate to regulate the recruitment and activity of RNA polymerase II in the beta-globin gene locus
Abstract
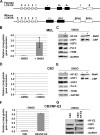
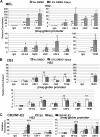
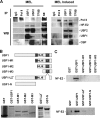
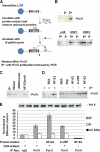
The human beta-globin gene is expressed at high levels in erythroid cells and regulated by proximal and distal cis-acting DNA elements, including promoter, enhancer, and a locus control region (LCR). Transcription complexes are recruited not only to the globin gene promoters but also to the LCR. Previous studies have implicated the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor USF and the tissue-restricted activator NF-E2 in the recruitment of transcription complexes to the beta-globin gene locus. Here we demonstrate that although USF is required for the efficient association of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) with immobilized LCR templates, USF and NF-E2 together regulate the association of Pol II with the adult beta-globin gene promoter. Recruitment of Pol II to the LCR occurs in undifferentiated murine erythroleukemia cells, but phosphorylation of LCR-associated Pol II at serine 5 of the C-terminal domain is mediated by erythroid differentiation and requires the activity of NF-E2. Furthermore, we provide evidence showing that USF interacts with NF-E2 in erythroid cells. The data provide mechanistic insight into how ubiquitous and tissue-restricted transcription factors cooperate to regulate the recruitment and activity of transcription complexes in a tissue-specific chromatin domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The beta -globin locus control region (LCR) functions primarily by enhancing the transition from transcription initiation to elongation.Genes Dev. 2003 Apr 15;17(8):1009-18. doi: 10.1101/gad.1072303. Epub 2003 Apr 2. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12672691 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the function of the adult β-globin downstream promoter region using an artificial zinc finger DNA-binding domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(7):4363-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku107. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24497190 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of beta-major globin gene transcription is associated with recruitment of NF-E2 to the beta-globin LCR and gene promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 28;98(18):10226-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.181344198. Epub 2001 Aug 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11517325 Free PMC article.
-
ChIPs of the beta-globin locus: unraveling gene regulation within an active domain.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002 Apr;12(2):170-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00283-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002. PMID: 11893490 Review.
-
Joining the loops: beta-globin gene regulation.IUBMB Life. 2008 Dec;60(12):824-33. doi: 10.1002/iub.129. IUBMB Life. 2008. PMID: 18767169 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-cycle specific association of transcription factors and RNA polymerase ii with the human β-globin gene locus.J Cell Biochem. 2013 Sep;114(9):1997-2006. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24542. J Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23519692 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-363 and GATA-1 are regulated by HIF-1α in K562 cells under hypoxia.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Sep;14(3):2503-10. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5578. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27485543 Free PMC article.
-
An expansive human regulatory lexicon encoded in transcription factor footprints.Nature. 2012 Sep 6;489(7414):83-90. doi: 10.1038/nature11212. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22955618 Free PMC article.
-
The distinctive roles of erythroid specific activator GATA-1 and NF-E2 in transcription of the human fetal γ-globin genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Sep 1;39(16):6944-55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr253. Epub 2011 May 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21609963 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of hundreds of cis-regulatory landscapes at high resolution in a single, high-throughput experiment.Nat Genet. 2014 Feb;46(2):205-12. doi: 10.1038/ng.2871. Epub 2014 Jan 12. Nat Genet. 2014. PMID: 24413732
References
-
- Felsenfeld G., Groudine M. (2003) Nature 421, 448–453 - PubMed
-
- Chakalova L., Debrand E., Mitchell J. A., Osborne C. S., Fraser P. (2005) Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 669–677 - PubMed
-
- Sutherland H., Bickmore W. A. (2009) Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 457–466 - PubMed
-
- Loose M., Swiers G., Patient R. (2007) Curr. Opin. Hematol. 14, 307–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

