Inhibition of dengue virus polymerase by blocking of the RNA tunnel
- PMID: 20237086
- PMCID: PMC2876596
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02451-09
Inhibition of dengue virus polymerase by blocking of the RNA tunnel
Abstract
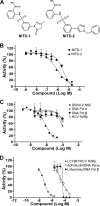
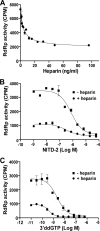
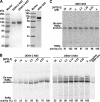
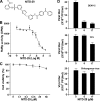
Dengue virus (DENV) is the most prevalent mosquito-borne viral pathogen in humans. Neither vaccine nor antiviral therapy is currently available for DENV. We report here that N-sulfonylanthranilic acid derivatives are allosteric inhibitors of DENV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The inhibitor was identified through high-throughput screening of one million compounds using a primer extension-based RdRp assay [substrate poly(C)/oligo(G)(20)]. Chemical modification of the initial "hit" improved the compound potency to an IC(50) (that is, a concentration that inhibits 50% RdRp activity) of 0.7 microM. In addition to suppressing the primer extension-based RNA elongation, the compound also inhibited de novo RNA synthesis using a DENV subgenomic RNA, but at a lower potency (IC(50) of 5 microM). Remarkably, the observed anti-polymerase activity is specific to DENV RdRp; the compound did not inhibit WNV RdRp and exhibited IC(50)s of >100 microM against hepatitis C virus RdRp and human DNA polymerase alpha and beta. UV cross-linking and mass spectrometric analysis showed that a photoreactive inhibitor could be cross-linked to Met343 within the RdRp domain of DENV NS5. On the crystal structure of DENV RdRp, Met343 is located at the entrance of RNA template tunnel. Biochemical experiments showed that the order of addition of RNA template and inhibitor during the assembly of RdRp reaction affected compound potency. Collectively, the results indicate that the compound inhibits RdRp through blocking the RNA tunnel. This study has provided direct evidence to support the hypothesis that allosteric pockets from flavivirus RdRp could be targeted for antiviral development.
Figures


References
-
- Ackermann, M., and R. Padmanabhan. 2001. De novo synthesis of RNA by the dengue virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase exhibits temperature dependence at the initiation but not elongation phase. J. Biol. Chem. 276:39926-39937. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu, P. L. 2007. Non-nucleoside inhibitors of the HCV NS5B polymerase: progress in the discovery and development of novel agents for the treatment of HCV infections. Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs. 8:614-634. - PubMed
-
- Best, S. M., K. L. Morris, J. G. Shannon, S. J. Robertson, D. N. Mitzel, G. S. Park, E. Boer, J. B. Wolfinbarger, and M. E. Bloom. 2005. Inhibition of interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling by a tick-borne flavivirus and identification of NS5 as an interferon antagonist. J. Virol. 79:12828-12839. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswal, B. K., M. Wang, M. M. Cherney, L. Chan, C. G. Yannopoulos, D. Bilimoria, J. Bedard, and M. N. James. 2006. Non-nucleoside inhibitors binding to hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase reveal a novel mechanism of inhibition. J. Mol. Biol. 361:33-45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

