Human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7 upregulation of nucleophosmin is important for proliferation and inhibition of differentiation
- PMID: 20237089
- PMCID: PMC2863842
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01965-09
Human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7 upregulation of nucleophosmin is important for proliferation and inhibition of differentiation
Abstract
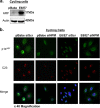
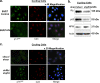
The E6 and E7 oncoproteins of high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPVs) are together sufficient to cause cellular transformation. Nucleophosmin (NPM) was identified as a protein with increased levels in two-dimensional (2-D) gel analysis of human foreskin keratinocytes (HFKs) expressing E7 following methylcellulose-induced differentiation. Analysis of NPM expression in E7-expressing cells and E6- and E7-expressing cells in culture and in organotypic rafts confirmed the increased levels observed in 2-D gel analysis. The elevated expression of NPM was determined to be posttranscriptional and was attributed to increased v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene (AKT) activity in the E6- and E7-expressing cells. Depletion of NPM caused a reduction in the replicative capacity of E7- and E6/E7-expressing HFKs and an increase in markers of differentiation. Also, the p53 and pRb tumor suppressor levels are increased with the knockdown of NPM in E6/E7-expressing cells, and, interestingly, p14(ARF) is relocalized from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm in these cells. The results show for the first time that NPM is required for the proliferation and inhibition of differentiation observed in HPV E6- and E7-expressing primary cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of microRNA-mRNA Target Pairs by Human Papillomavirus 16 Oncoproteins.mBio. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):e02170-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02170-16. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28049151 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs dysregulated in human foreskin keratinocytes (HFKs) expressing the human papillomavirus (HPV) Type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins.Microrna. 2013;2(1):2-13. doi: 10.2174/2211536611302010002. Microrna. 2013. PMID: 25070710
-
MicroRNA 203 expression in keratinocytes is dependent on regulation of p53 levels by E6.J Virol. 2010 Oct;84(20):10644-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00703-10. Epub 2010 Aug 11. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20702634 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular basis of cervical carcinogenesis by high-risk human papillomaviruses].Uirusu. 2008 Dec;58(2):141-54. doi: 10.2222/jsv.58.141. Uirusu. 2008. PMID: 19374192 Review. Japanese.
-
Papillomavirus E6 and E7 proteins and their cellular targets.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:1003-17. doi: 10.2741/2739. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981607 Review.
Cited by
-
Host Factor Nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1/B23) Exerts Antiviral Effects against Chikungunya Virus by Its Interaction with Viral Nonstructural Protein 3.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0537122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05371-22. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37409962 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and identification of human cervical cancer cell line C33A stably expressing human papillomavirus type 58 E6E7 fusion gene].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 25;34(4):578-584. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201605040. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29745555 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Telomeres and Telomerase During Human Papillomavirus-Induced Carcinogenesis.Mol Diagn Ther. 2018 Aug;22(4):421-430. doi: 10.1007/s40291-018-0336-x. Mol Diagn Ther. 2018. PMID: 29777397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of globular heads of the C1q receptor in HPV 16 E2-induced human cervical squamous carcinoma cell apoptosis is associated with p38 MAPK/JNK activation.J Transl Med. 2013 May 8;11:118. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-118. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23651874 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Linear Relationship between Nucleophosmin Protein Expression and the Viral Load in HPV-Associated Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Possible Tool for Stratification of Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 9;24(4):3482. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043482. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cobrinik, D., S. F. Dowdy, P. W. Hinds, S. Mittnacht, and R. A. Weinberg. 1992. The retinoblastoma protein and the regulation of cell cycling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17:312-315. - PubMed
-
- Colombo, E., J. C. Marine, D. Danovi, B. Falini, and P. G. Pelicci. 2002. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:529-533. - PubMed
-
- Dyson, N., P. M. Howley, K. Munger, and E. Harlow. 1989. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science 243:934-937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

