Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry fingerprinting
- PMID: 20237093
- PMCID: PMC2863888
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01831-09
Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry fingerprinting
Abstract
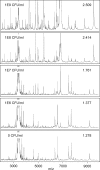
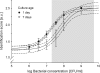
Early and adequate antimicrobial therapy has been shown to improve the clinical outcome in bloodstream infections (BSI). To provide rapid pathogen identification for targeted treatment, we applied matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry fingerprinting to bacteria directly recovered from blood culture bottles. A total of 304 aerobic and anaerobic blood cultures, reported positive by a Bactec 9240 system, were subjected in parallel to differential centrifugation with subsequent mass spectrometry fingerprinting and reference identification using established microbiological methods. A representative spectrum of bloodstream pathogens was recovered from 277 samples that grew a single bacterial isolate. Species identification by direct mass spectrometry fingerprinting matched reference identification in 95% of these samples and worked equally well for aerobic and anaerobic culture bottles. Application of commonly used score cutoffs to classify the fingerprinting results led to an identification rate of 87%. Mismatching mostly resulted from insufficient bacterial numbers and preferentially occurred with Gram-positive samples. The respective spectra showed low concordance to database references and were effectively rejected by score thresholds. Spiking experiments and examination of the respective study samples even suggested applicability of the method to mixed cultures. With turnaround times around 100 min, the approach allowed for reliable pathogen identification at the day of blood culture positivity, providing treatment-relevant information within the critical phase of septic illness.
Figures
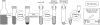
Similar articles
-
The sensitivity of direct identification from positive BacT/ALERT™ (bioMérieux) blood culture bottles by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry is low.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Feb;17(2):192-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03229.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 20370799
-
Direct identification of bacteria from positive BacT/ALERT blood culture bottles using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Nov;80(3):193-6. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25139844
-
Microorganisms direct identification from blood culture by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Apr;17(4):546-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03257.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 20456452
-
Use of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for identification of bacteria that are difficult to culture.J Microbiol Methods. 2013 Jan;92(1):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Microbiol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23154044 Review.
-
Detection of microorganisms in blood specimens using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: a review.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Nov;16(11):1620-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03290.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20545958 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Microflex LT and Vitek MS systems for routine identification of bacteria by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Apr;50(4):1313-25. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05971-11. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22322345 Free PMC article.
-
Improving timelines in reporting results from positive blood cultures: simulation of impact of rapid identification on therapy on a real-life cohort.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Dec;37(12):2253-2260. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3366-8. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30187248
-
Same day identification and full panel antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles made possible by a combined lysis-filtration method with MALDI-TOF VITEK mass spectrometry and the VITEK2 system.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 14;9(2):e87870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087870. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24551067 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated bacterial detection in blood culture by enhanced acoustic flow cytometry (AFC) following peptide nucleic acid fluorescence in situ hybridization (PNA-FISH).PLoS One. 2019 Feb 8;14(2):e0201332. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201332. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30735489 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evaluation of the FilmArray blood culture identification panel in identification of bacteria and yeasts from positive blood culture bottles.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Dec;51(12):4130-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01835-13. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24088863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bearman, G. M. L., and R. P. Wenzel. 2005. Bacteremias: a leading cause of death. Arch. Med. Res. 36:646-659. - PubMed
-
- Carbonnelle, E., J.-L. Beretti, S. Cottyn, G. Quesne, P. Berche, X. Nassif, and A. Ferroni. 2007. Rapid identification of staphylococci isolated in clinical microbiology laboratories by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:2156-2161. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, F. Y., J. E. Peacock, Jr., D. M. Musher, P. Triplett, B. B. MacDonald, J. M. Mylotte, A. O'Donnell, M. M. Wagener, and V. L. Yu. 2003. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: recurrence and the impact of antibiotic treatment in a prospective multicenter study. Medicine (Baltimore) 82:333-339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

