Sex differences in epigenetic regulation of the estrogen receptor-alpha promoter within the developing preoptic area
- PMID: 20237133
- PMCID: PMC2869250
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-0649
Sex differences in epigenetic regulation of the estrogen receptor-alpha promoter within the developing preoptic area
Abstract
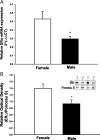
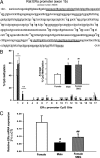
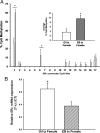
Sex differences in the brain are largely organized by a testicular hormone surge that occurs in males shortly after birth. Although this hormone surge is transient, sex differences in brain and behavior are lasting. Here we describe a sex difference in DNA methylation of the estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) promoter region within the developing rat preoptic area, with males exhibiting more DNA methylation within the ERalpha promoter than females. More importantly, we report that simulating maternal grooming, a form of maternal interaction that is sexually dimorphic with males experiencing more than females during the neonatal period, effectively masculinizes female ERalpha promoter methylation and gene expression. This suggests natural variations in maternal care that are directed differentially at males vs. females can influence sex differences in the brain by creating sexually dimorphic DNA methylation patterns. We also find that the early estradiol exposure may contribute to sex differences in DNA methylation patterns. This suggests that early social interaction and estradiol exposure may converge at the genome to organize lasting sex differences in the brain via epigenetic differentiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic impact of simulated maternal grooming on estrogen receptor alpha within the developing amygdala.Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Oct;25(7):1299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2011.02.009. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Brain Behav Immun. 2011. PMID: 21352906 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal care associated with methylation of the estrogen receptor-alpha1b promoter and estrogen receptor-alpha expression in the medial preoptic area of female offspring.Endocrinology. 2006 Jun;147(6):2909-15. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1119. Epub 2006 Mar 2. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16513834
-
Estrogen receptor {alpha} gene promoter 0/B usage in the rat sexually dimorphic nucleus of the preoptic area.Endocrinology. 2010 Apr;151(4):1923-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1022. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20185767
-
Epigenetic mechanisms are involved in sexual differentiation of the brain.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012 Sep;13(3):163-71. doi: 10.1007/s11154-012-9202-z. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012. PMID: 22327342 Review.
-
Estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression in the cortex: sex differences during development and in adulthood.Horm Behav. 2011 Mar;59(3):353-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 20713055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic mechanisms in pubertal brain maturation.Neuroscience. 2014 Apr 4;264:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.014. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24239720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and epigenetic underpinnings of sex differences in the brain and in neurological and psychiatric disease susceptibility.Prog Brain Res. 2010;186:77-95. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53630-3.00006-3. Prog Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 21094887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of sexual differentiation in the mammalian nervous system.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Jan;40:67-86. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26790970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of a bisphenol A, F, and S mixture and maternal care on the brain transcriptome of rat dams and pups.Neurotoxicology. 2022 Dec;93:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2022.08.014. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Neurotoxicology. 2022. PMID: 36041667 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying Sex Differences in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 19;14(1):98. doi: 10.3390/biology14010098. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rhoda J, Corbier P, Roffi J 1984 Gonadal steroid concentrations in serum and hypothalamus of the rat at birth: aromatization of testosterone to 17β-estradiol. Endocrinology 114:1754–1760 - PubMed
-
- Pang SF, Caggiula AR, Gay VL, Goodman RL, Pang CS 1979 Serum concentrations of testosterone, oestrogens, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone in male and female rats during the critical period of neural sexual differentiation. J Endocrinol 80:103–110 - PubMed
-
- Weisz J, Ward IL 1980 Plasma testosterone and progesterone titers of pregnant rats, their male and female fetuses, and neonatal offspring. Endocrinology 106:306–316 - PubMed
-
- Olesen KM, Jessen HM, Auger CJ, Auger AP 2005 Dopaminergic activation of estrogen receptors in neonatal brain alters progestin receptor expression and juvenile social play behavior. Endocrinology 146:3705–3712 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

