Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and GEF-H1 mediate depolarization-induced Rho activation and paracellular permeability increase
- PMID: 20237148
- PMCID: PMC3226803
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00408.2009
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and GEF-H1 mediate depolarization-induced Rho activation and paracellular permeability increase
Abstract
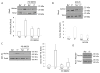
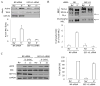
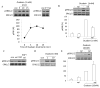
Plasma membrane depolarization activates the Rho/Rho kinase (ROK) pathway and thereby enhances myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation, which in turn is thought to be a key regulator of paracellular permeability. However, the upstream mechanisms that couple depolarization to Rho activation and permeability changes are unknown. Here we show that three different depolarizing stimuli (high extracellular K(+) concentration, the lipophilic cation tetraphenylphosphonium, or l-alanine, which is taken up by electrogenic Na(+) cotransport) all provoke robust phosphorylation of ERK in LLC-PK1 and Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. Importantly, inhibition of ERK prevented the depolarization-induced activation of Rho. Searching for the underlying mechanism, we have identified the GTP/GDP exchange factor GEF-H1 as the ERK-regulated critical exchange factor responsible for the depolarization-induced Rho activation. This conclusion is based on our findings that 1) depolarization activated GEF-H1 but not p115RhoGEF, 2) short interfering RNA-mediated GEF-H1 silencing eliminated the activation of the Rho pathway, and 3) ERK inhibition prevented the activation of GEF-H1. Moreover, we found that the Na(+)-K(+) pump inhibitor ouabain also caused ERK, GEF-H1, and Rho activation, partially due to its depolarizing effect. Regarding the functional consequences of this newly identified pathway, we found that depolarization increased paracellular permeability in LLC-PK1 and MDCK cells and that this effect was mitigated by inhibiting myosin using blebbistatin or a dominant negative (phosphorylation incompetent) MLC. Taken together, we propose that the ERK/GEF-H1/Rho/ROK/pMLC pathway could be a central mechanism whereby electrogenic transmembrane transport processes control myosin phosphorylation and regulate paracellular transport in the tubular epithelium.
Figures




References
-
- Ark M, Kubat H, Beydagi H, Ergenoglu T, Songu-Mize E. Involvement of rho kinase in the ouabain-induced contractions of the rat renal arteries. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340:417–421. - PubMed
-
- Arya R, Mallik M, Lakhotia SC. Heat shock genes - integrating cell survival and death. J Biosci. 2007;32:595–610. - PubMed
-
- Baldassa S, Zippel R, Sturani E. Depolarization-induced signaling to Ras, Rap1 and MAPKs in cortical neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003;119:111–122. - PubMed
-
- Balestrino M. Pathophysiology of anoxic depolarization: new findings and a working hypothesis. J Neurosci Methods. 1995;59:99–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

