HSP90 protein stabilizes unloaded argonaute complexes and microscopic P-bodies in human cells
- PMID: 20237157
- PMCID: PMC2861606
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-10-0885
HSP90 protein stabilizes unloaded argonaute complexes and microscopic P-bodies in human cells
Abstract
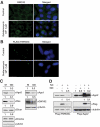
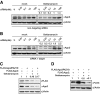
Key components of the miRNA-mediated gene regulation pathway are localized in cytoplasmic processing bodies (P-bodies). Mounting evidence suggests that the presence of microscopic P-bodies are not always required for miRNA-mediated gene regulation. Here we have shown that geldanamycin, a well-characterized HSP90 inhibitor, abolishes P-bodies and significantly reduces Argonaute and GW182 protein levels but does not affect the miRNA level and the efficiency of miRNA-mediated gene repression; however, it significantly impairs siRNA loading and the efficacy of exogenous siRNA. Our data suggests that HSP90 protein chaperones Argonautes before binding RNA and may facilitate efficient loading of small RNA.
Figures


References
-
- Banerji U., Walton M., Raynaud F., Grimshaw R., Kelland L., Valenti M., Judson I., Workman P. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships for the heat shock protein 90 molecular chaperone inhibitor 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin in human ovarian cancer xenograft models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005;11:7023–7032. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya S. N., Habermacher R., Martine U., Closs E. I., Filipowicz W. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell. 2006;125:1111–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

