Endogenous RhoG is rapidly activated after epidermal growth factor stimulation through multiple guanine-nucleotide exchange factors
- PMID: 20237158
- PMCID: PMC2861620
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0809
Endogenous RhoG is rapidly activated after epidermal growth factor stimulation through multiple guanine-nucleotide exchange factors
Erratum in
- Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 15;22(14):2659
Abstract
RhoG is a member of the Rac-like subgroup of Rho GTPases and has been linked to a variety of different cellular functions. Nevertheless, many aspects of RhoG upstream and downstream signaling remain unclear; in particular, few extracellular stimuli that modulate RhoG activity have been identified. Here, we describe that stimulation of epithelial cells with epidermal growth factor leads to strong and rapid activation of RhoG. Importantly, this rapid activation was not observed with other growth factors tested. The kinetics of RhoG activation after epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation parallel the previously described Rac1 activation. However, we show that both GTPases are activated independently of one another. Kinase inhibition studies indicate that the rapid activation of RhoG and Rac1 after EGF treatment requires the activity of the EGF receptor kinase, but neither phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase nor Src kinases. By using nucleotide-free RhoG pull-down assays and small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown studies, we further show that guanine-nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) of the Vav family mediate EGF-induced rapid activation of RhoG. In addition, we found that in certain cell types the recently described RhoG GEF PLEKHG6 can also contribute to the rapid activation of RhoG after EGF stimulation. Finally, we present results that show that RhoG has functions in EGF-stimulated cell migration and in regulating EGF receptor internalization.
Figures
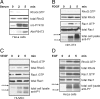
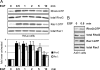


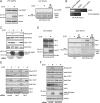
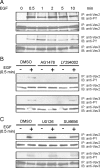


References
-
- Araki N., Egami Y., Watanabe Y., Hatae T. Phosphoinositide metabolism during membrane ruffling and macropinosome formation in EGF-stimulated A431 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2007;313:1496–1507. - PubMed
-
- Beier I., Dusing R., Vetter H., Schmitz U. Epidermal growth factor stimulates Rac1 and p21-activated kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 2008;196:92–97. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand-Duchesne M. P., Grenier D., Gagnon G. Epidermal growth factor released from platelet-rich plasma promotes endothelial cell proliferation in vitro. J. Periodontal Res. 2010;45:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Blangy A., Vignal E., Schmidt S., Debant A., Gauthier-Rouviere C., Fort P. TrioGEF1 controls Rac- and Cdc42-dependent cell structures through the direct activation of rhoG. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:729–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

