Chemerin, a novel adipokine in the regulation of angiogenesis
- PMID: 20237162
- PMCID: PMC2869547
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-0042
Chemerin, a novel adipokine in the regulation of angiogenesis
Abstract
Context: Chemerin is a new adipokine associated with obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Gene expression levels of chemerin were elevated in the adipose depots of obese compared with lean animals and was markedly elevated during differentiation of fibroblasts into mature adipocytes.
Objective: The objective of the study was to identify factors that affect the regulation and potential function of chemerin using a genetics approach.
Design, setting, patients, and intervention: Plasma chemerin levels were measured in subjects from the San Antonio Family Heart Study, a large family-based genetic epidemiological study including 1354 Mexican-American individuals. Individuals were randomly sampled without regard to phenotype or disease status.
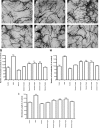
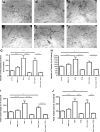
Main outcome measures: A genome-wide association analysis using 542,944 single-nucleotide polymorphisms in a subset of 523 of the same subjects was undertaken. The effect of chemerin on angiogenesis was measured using human endothelial cells and interstitial cells in coculture in a specially formulated medium.
Results: Serum chemerin levels were found to be highly heritable (h(2) = 0.25; P = 1.4 x 10(-9)). The single-nucleotide polymorphism showing strongest evidence of association (rs347344; P = 1.4 x 10(-6)) was located within the gene encoding epithelial growth factor-like repeats and discoidin I-like domains 3, which has a known role in angiogenesis. Functional angiogenesis assays in human endothelial cells confirmed that chemerin significantly mediated the formation of blood vessels to a similar extent as vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conclusion: Here we demonstrate for the first time that plasma chemerin levels are significantly heritable and identified a novel role for chemerin as a stimulator of angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Wittamer V, Grégoire F, Robberecht P, Vassart G, Communi D, Parmentier M 2004 The C-terminal nonapeptide of mature chemerin activates the chemerin receptor with low nanomolar potency. J Biol Chem 279:9956–9962 - PubMed
-
- Zabel BA, Allen SJ, Kulig P, Allen JA, Cichy J, Handel TM, Butcher EC 2005 Chemerin activation by serine proteases of the coagulation, fibrinolytic, and inflammatory cascades. J Biol Chem 280:34661–34666 - PubMed
-
- Wittamer V, Franssen JD, Vulcano M, Mirjolet JF, Le Poul E, Migeotte I, Brézillon S, Tyldesley R, Blanpain C, Detheux M, Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Vassart G, Parmentier M, Communi D 2003 Specific recruitment of antigen-presenting cells by chemerin, a novel processed ligand from human inflammatory fluids. J Exp Med 198:977–985 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zabel BA, Ohyama T, Zuniga L, Kim JY, Johnston B, Allen SJ, Guido DG, Handel TM, Butcher EC 2006 Chemokine-like receptor 1 expression by macrophages in vivo: regulation by TGF-β and TLR ligands. Exp Hematol 34:1106–1114 - PubMed
-
- Zabel BA, Zuniga L, Ohyama T, Allen SJ, Cichy J, Handel TM, Butcher EC 2006 Chemoattractants, extracellular proteases, and the integrated host defense response. Exp Hematol 34:1021–1032 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

