Impaired ganglioside metabolism in Huntington's disease and neuroprotective role of GM1
- PMID: 20237277
- PMCID: PMC6632269
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6348-09.2010
Impaired ganglioside metabolism in Huntington's disease and neuroprotective role of GM1
Abstract
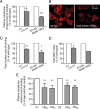
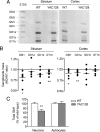
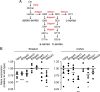
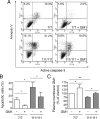
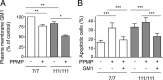
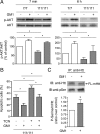
Huntington's disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the expansion of a polyglutamine stretch in the protein huntingtin (Htt). HD neurons are dysfunctional at multiple levels and have increased susceptibility to stress and apoptotic stimuli. We have discovered that synthesis of the ganglioside GM1 is reduced in fibroblasts from HD patients and in cell and animal models of HD, and that decreased GM1 levels contribute to heighten HD cell susceptibility to apoptosis. The apoptotic susceptibility is recapitulated through inhibition of ganglioside synthesis in wild-type striatal cells, suggesting that decreased GM1 levels might be one of the key events leading to HD pathogenesis and progression. Administration of GM1 restores ganglioside levels in HD cells and promotes activation of AKT and phosphorylation of mutant Htt, leading to decreased mutant Htt toxicity and increased survival of HD cells. Our data identify GM1 as a potential treatment for HD.
Figures

References
-
- Abad-Rodriguez J, Robotti A. Regulation of axonal development by plasma membrane gangliosides. J Neurochem. 2007;103(Suppl 1):47–55. - PubMed
-
- Alter M. GM1 ganglioside for acute ischemic stroke. Trial design issues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;845:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Bae BI, Xu H, Igarashi S, Fujimuro M, Agrawal N, Taya Y, Hayward SD, Moran TH, Montell C, Ross CA, Snyder SH, Sawa A. p53 mediates cellular dysfunction and behavioral abnormalities in Huntington's disease. Neuron. 2005;47:29–41. - PubMed
-
- Chiavegatto S, Sun J, Nelson RJ, Schnaar RL. A functional role for complex gangliosides: motor deficits in GM2/GD2 synthase knockout mice. Exp Neurol. 2000;166:227–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
