Growth hormone rescues hippocampal synaptic function after sleep deprivation
- PMID: 20237303
- PMCID: PMC3774423
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00580.2009
Growth hormone rescues hippocampal synaptic function after sleep deprivation
Abstract
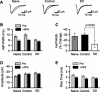
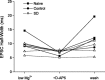
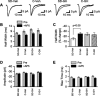
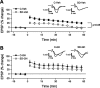
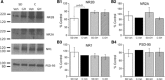
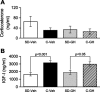
Sleep is required for, and sleep loss impairs, normal hippocampal synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor function and expression, hippocampal NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity, and hippocampal-dependent memory function. Although sleep is essential, the signals linking sleep to hippocampal function are not known. One potential signal is growth hormone. Growth hormone is released during sleep, and its release is suppressed during sleep deprivation. If growth hormone links sleep to hippocampal function, then restoration of growth hormone during sleep deprivation should prevent adverse consequences of sleep loss. To test this hypothesis, we examined rat hippocampus for spontaneous excitatory synaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons, long-term potentiation in area CA1, and NMDA receptor subunit proteins in synaptic membranes. Three days of sleep deprivation caused a significant reduction in NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents compared with control treatments. When rats were injected with growth hormone once per day during sleep deprivation, the loss of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic currents was prevented. Growth hormone injections also prevented the impairment of long-term potentiation that normally follows sleep deprivation. In addition, sleep deprivation led to a selective loss of NMDA receptor 2B (NR2B) from hippocampal synaptic membranes, but normal NR2B expression was restored by growth hormone injection. Our results identify growth hormone as a critical mediator linking sleep to normal synaptic function of the hippocampus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation decreases long-term potentiation stability and affects some glutamatergic signaling proteins during hippocampal development.Neuroscience. 2008 Apr 22;153(1):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.072. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18359575 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep deprivation-induced alterations in excitatory synaptic transmission in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2006 Feb 1;570(Pt 3):553-65. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.093781. Epub 2005 Dec 1. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16322058 Free PMC article.
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation in CA1 region affects synaptic expression of glutamate receptor subunits and associated proteins in the whole hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2006 Sep 1;141(3):1399-413. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.04.070. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16766131
-
The tired hippocampus: the molecular impact of sleep deprivation on hippocampal function.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017 Jun;44:13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28242433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity, hippocampal place cells, and cognitive maps.Arch Neurol. 2001 Jun;58(6):874-81. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.6.874. Arch Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11405801 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth Hormone Alters Remapping in the Hippocampal Area CA1 in a Novel Environment.eNeuro. 2025 Feb 11;12(2):ENEURO.0237-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0237-24.2024. Print 2025 Feb. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 39900507 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advancements in Treating Sleep Disorders in Co-Occurring PTSD.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018 Jun 21;20(7):48. doi: 10.1007/s11920-018-0916-9. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2018. PMID: 29931537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acromegalic Rat Model Presented Cognitive Impairments and Tau Hyperphosphorylation in the Hippocampus.Neuroendocrinology. 2024;114(6):577-588. doi: 10.1159/000537813. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Neuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38368872 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal growth hormone modulates relational memory and the dendritic spine density in CA1.Learn Mem. 2020 Jan 16;27(2):33-44. doi: 10.1101/lm.050229.119. Print 2020 Feb. Learn Mem. 2020. PMID: 31949035 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxic saboteurs: straws that break the hippo's (hippocampus) back drive cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's Disease.Neurotox Res. 2013 Oct;24(3):407-59. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9407-2. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Neurotox Res. 2013. PMID: 23820984 Review.
References
-
- Arwert LI, Deijen JB, Müller M, Drent ML. Long-term growth hormone treatment preserves GH-induced memory and mood improvements: a 10-year follow-up study in GH-deficient adult men. Horm Behav 47: 343–349, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Malinow R. NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII. Neuron 48: 289–301, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361: 31–39, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Brandenberger G, Gronfier C, Chapotot F, Simon C, Piquard F. Effect of sleep deprivation on overall 24 h growth-hormone secretion. Lancet 356: 1408, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

