A nucleator arms race: cellular control of actin assembly
- PMID: 20237478
- PMCID: PMC2929822
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2867
A nucleator arms race: cellular control of actin assembly
Abstract
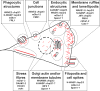
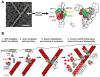
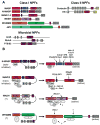
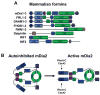
For over a decade, the actin-related protein 2/3 (ARP2/3) complex, a handful of nucleation-promoting factors and formins were the only molecules known to directly nucleate actin filament formation de novo. However, the past several years have seen a surge in the discovery of mammalian proteins with roles in actin nucleation and dynamics. Newly recognized nucleation-promoting factors, such as WASP and SCAR homologue (WASH), WASP homologue associated with actin, membranes and microtubules (WHAMM), and junction-mediating regulatory protein (JMY), stimulate ARP2/3 activity at distinct cellular locations. Formin nucleators with additional biochemical and cellular activities have also been uncovered. Finally, the Spire, cordon-bleu and leiomodin nucleators have revealed new ways of overcoming the kinetic barriers to actin polymerization.
Figures

References
-
- Goley ED, Welch MD. The ARP2/3 complex: an actin nucleator comes of age. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:713–726. - PubMed
-
- Chesarone MA, DuPage AG, Goode BL. Unleashing formins to remodel the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:62–74. - PubMed
-
- Stradal TE, Scita G. Protein complexes regulating Arp2/3-mediated actin assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:4–10. - PubMed
-
- Goley ED, Rodenbusch SE, Martin AC, Welch MD. Critical conformational changes in the Arp2/3 complex are induced by nucleotide and nucleation promoting factor. Mol Cell. 2004;16:269–279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

