L1CAM malfunction in the nervous system and human carcinomas
- PMID: 20237819
- PMCID: PMC11115577
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0339-1
L1CAM malfunction in the nervous system and human carcinomas
Abstract
Research over the last 25 years on the cell adhesion molecule L1 has revealed its pivotal role in nervous system function. Mutations of the human L1CAM gene have been shown to cause neurodevelopmental disorders such as X-linked hydrocephalus, spastic paraplegia and mental retardation. Impaired L1 function has been also implicated in the aetiology of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, defective enteric nervous system development and malformations of the renal system. Importantly, aberrant expression of L1 has emerged as a critical factor in the development of human carcinomas, where it enhances cell proliferation, motility and chemoresistance. This discovery promoted collaborative work between tumour biologists and neurobiologists, which has led to a substantial expansion of the basic knowledge about L1 function and regulation. Here we provide an overview of the pathological conditions caused by L1 malfunction. We further discuss how the available data on gene regulation, molecular interactions and posttranslational processing of L1 may contribute to a better understanding of associated neurological and cancerous diseases.
Figures
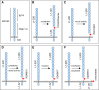
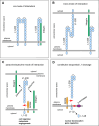
References
-
- Maness PF, Schachner M. Neural recognition molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily: signaling transducers of axon guidance and neuronal migration. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Fransen E, Van Camp G, Vits L, Willems PJ. L1-associated diseases: clinical geneticists divide, molecular geneticists unite. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:1625–1632. - PubMed
-
- Kanemura Y, Okamoto N, Sakamoto H, Shofuda T, Kamiguchi H, Yamasaki M. Molecular mechanisms and neuroimaging criteria for severe L1 syndrome with X-linked hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2006;105:403–412. - PubMed
-
- Weller S, Gärtner J. Genetic and clinical aspects of X-linked hydrocephalus (L1 disease): mutations in the L1CAM gene. Hum Mutat. 2001;18:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

