The small round blue cell tumors of the sinonasal area
- PMID: 20237994
- PMCID: PMC2825526
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-009-0158-6
The small round blue cell tumors of the sinonasal area
Abstract
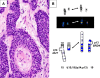
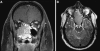
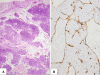
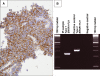
The diagnostic classification of small round blue cell tumors of the sinonasal area to include diverse malignancies of epithelial, hematolymphoid, neuroectodermal, and mesenchymal origin is challenging to the surgical pathologist using conventional histopathologic approaches because the cytomorphologic features are often overlapping or indistinctive. Rare or occasional clinical presentations in atypical age groups or unusual locations, as well as small biopsy samples may further complicate the differential diagnosis. Immunohistochemistry represents an extensively investigated ancillary technique that may aid in the provision of a definitive diagnosis. In recent years, certain small round blue cell tumors have been shown by cytogenetic analysis to have specific and primary chromosomal alterations, providing clinicians with a valuable tool to enhance their diagnostic armamentarium. The addition of molecular cytogenetic [fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)] and molecular pathologic [polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR] approaches has further enhanced the sensitivity and accuracy of detecting these genetic alterations including assessment in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Establishing an accurate diagnosis of a small round blue cell tumor of the sinonasal tract frequently requires adjunctive studies including immunohistochemical and molecular analyses.
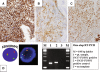
Figures
References
-
- Barnes L, Everson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D (eds) (2005) Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Kleihues P, Sobin LH, series eds. World health organization classification of tumours. Lyon, France: IARC Press.
-
- Franchi A, Moroni M, Massi D, et al. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, nasopharyngeal-type undifferentiated carcinoma, and keratinizing and nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma express different cytokeratin patterns. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:1597–1604. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200212000-00007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

